Monthly Shaarli
June, 2024

Témoignages. Dans l’enfer des “nettoyeurs” des réseaux sociaux
Alors que les géants du numérique tentent de renforcer le contrôle sur leurs plateformes, les “modérateurs de contenu” sont exposés à d’innombrables posts violents ou haineux dans le cadre leur travail. Le quotidien japonais “Asahi Shimbun” est allé à leur rencontre.
Publié le 27 juin 2024 à 05h00 Shiori Tabuchi, Azusa Ushio
Ces vidéos prolifèrent sur la Toile. Violences, menaces, actes sexuels… Pourtant, ils n’ont que deux ou trois minutes pour décider de les supprimer ou non.
Nous sommes dans un immeuble, dans une ville d’Asie du Sud-Est. Dans une salle, assis en silence devant leur ordinateur, casque sur les oreilles, des modérateurs de contenu, surnommés “nettoyeurs des réseaux sociaux”, suppriment les publications Internet jugées inappropriées.
Parmi eux, un Japonais, employé par un sous-traitant d’un géant du numérique qui exploite un site de partage de vidéos, a accepté de répondre à nos questions, à condition de ne divulguer ni son nom, ni son âge :
“On m’interdit de parler en détail du contenu de mon travail.”
Il travaille en trois-huit avec des équipes constituées par langue pour un salaire mensuel d’environ 200 000 yens [1 200 euros]. Soumis à une stricte confidentialité, il n’a pas le droit d’apporter son smartphone dans la salle, ni même un simple stylo.
Lorsqu’il arrive à son poste, il allume ses deux écrans. Sur l’un d’eux, une vidéo passe en vitesse rapide. L’autre affiche les nombreuses règles de modération à appliquer, un document qui semble faire un millier de pages. Lorsqu’il repère un contenu proscrit, il classe la vidéo dans une catégorie, par exemple “violence”, “porno”, “harcèlement” ou “haine”. Et cherche la règle qu’elle enfreint et copie cette dernière dans le champ des commentaires. “La chose essentielle est de la trouver aussi vite que possible”, explique-t-il.
Lorsqu’il a fini de vérifier une vidéo, la suivante apparaît. Outre les contenus signalés par des utilisateurs, “il y a probablement des publications détectées automatiquement par l’intelligence artificielle (IA), mais je ne sais pas comment elles sont choisies”.
Jeu du chat et de la souris
Si une vidéo montre une personne battue jusqu’au sang ou contient des menaces du genre “Je vais le tuer”, il la supprime immédiatement. En cas de doute, il envoie la vidéo à un service spécialisé. Sur les quelque 80 vidéos qu’il visionne par jour, il en supprime environ trois. Il y en a également une dizaine qu’il trouve difficiles à juger. Il ignore combien il y a de services au total, et qui prend les décisions en définitive. “Je procède de manière mécanique”, confie-t-il.
Il se souvient d’un pic d’activité après l’assassinat par balle de l’ancien Premier ministre Shinzo Abe [en juillet 2022]. Des images de la scène ont été publiées à de nombreuses reprises. “J’effaçais les vidéos non floutées pratiquement les unes après les autres.”
Les règles de modération sont nombreuses et détaillées, et les changements sont annoncés chaque semaine lors de réunions matinales. Est également fournie une base de données rassemblant les mots tabous. À la fin de chaque journée de travail, les modérateurs passent un test visant à évaluer leur connaissance des dernières règles : ceux qui obtiennent un faible score voient leur salaire réduit.
Les vidéos supprimées sont fréquemment republiées, et certains contenus passent entre les mailles du filet. Notre modérateur est conscient des critiques :
“Nous faisons de notre mieux, mais c’est comme le jeu du chat et de la souris. Nous ne pouvons pas effacer toutes les vidéos. Celles qui ne sont pas signalées restent.”
Le géant du numérique qui assure ce service de modération soutenait autrefois qu’il ne faisait que fournir un “lieu” d’expression et n’était pas responsable des contenus publiés. Mais la prolifération des publications nuisibles l’a contraint à réagir et à renforcer sa surveillance.
Le règlement sur les services numériques (Digital Services Act, DSA), adopté par l’Union européenne (UE), oblige aujourd’hui les grandes plateformes Internet à supprimer les publications nuisibles, notamment les contenus discriminatoires et les fausses informations. Si beaucoup sont supprimées automatiquement par l’IA, certaines nécessitent une intervention humaine. Selon les rapports que la Commission européenne a demandé aux géants du numériques de présenter en octobre dernier, Facebook a supprimé en Europe près de 47 millions de contenus contrevenant à la réglementation au cours des cinq mois qui ont suivi la fin avril 2023. Et 2,83 millions d’entre eux, soit 6 %, ont été supprimés par des modérateurs.
“Soldats des réseaux”
Facebook emploie environ 15 000 modérateurs et X environ 2 300. TikTok en compte environ 40 000, chargés notamment de contrôler les vidéos populaires qui dépassent un certain nombre de vues et de supprimer celles qui posent problème.
“Les modérateurs sont les soldats qui œuvrent dans l’ombre des réseaux sociaux”, estime Kauna Malgwi, 30 ans, qui vit aujourd’hui à Abuja, la capitale du Nigeria. Il y a cinq ans, alors qu’elle était une mère célibataire en situation précaire, elle est partie étudier au Kenya. Elle y a accepté ce qui était présenté comme un “poste d’interprète dans un ‘service clientèle’ utilisant le haoussa”, l’une des langues qui comptent le plus grand nombre de locuteurs en Afrique de l’Ouest. En réalité, elle s’est retrouvée modératrice pour Meta, qui exploite Facebook et Instagram. En parallèle à ses études de troisième cycle, pendant environ quatre ans, jusqu’en mars 2023, elle a travaillé neuf heures par jour, cinq jours par semaine, pour la succursale kenyane d’un sous-traitant du géant du numérique américain.
Expérience traumatisante
La première vidéo qu’elle a visionnée montrait un homme chutant du 15e étage d’un immeuble. Devant l’effroyable spectacle du corps s’écrasant au sol, elle a sauté de sa chaise. Elle devait remplir un questionnaire pyramidal énonçant les motifs de suppression du haut vers le bas. Après avoir répondu par la négative à la première question – “Voit-on des corps nus ?” –, elle a coché les cases “Voit-on des viscères ?” et “Voit-on du sang ?”.
Agressions sexuelles sur des enfants en bas âge, exécutions par des groupes extrémistes, suicides par balle… Chaque jour, elle examinait un millier de vidéos, détectées par l’IA ou signalées par des utilisateurs, et avait un maximum de cinquante-cinq secondes par vidéo pour décider de leur suppression ou non.
Elle supprimait également des textes à caractère raciste et d’autres messages de haine contenant des mots spécifiques.
“Il n’y avait pas que les textes. Par exemple, un dessin représentant un Asiatique et un singe côte à côte avec la légende ‘deux frères’ devait être supprimé.”
Elle a même supprimé des contenus publiés en Asie du Sud-Est, à plusieurs milliers de kilomètres de là.
Elle gagnait 60 000 shillings kényans (environ 400 euros) par mois, ce qui correspond au revenu mensuel moyen au Kenya. Mais elle souffrait à la fois d’insomnie et de trouble panique, ce qui l’a conduite plusieurs fois à l’hôpital.
Les accords de confidentialité ne lui ont même pas permis de se confier à sa famille. Ses collègues, les seuls avec lesquels elle pouvait partager ses sentiments, fumaient du cannabis pendant leurs pauses pour échapper à la réalité. Certains ont même avoué envisager le suicide. “C’est certes un travail important de protéger les nombreux utilisateurs de ces institutions que sont devenus les réseaux sociaux, mais quand même…” Aujourd’hui encore, il lui arrive de pleurer en repensant aux images qu’elle a vues.
DensePose From WiFi
Jiaqi Geng, Dong Huang, Fernando De la Torre 31 Dec 2022
Abstract
Advances in computer vision and machine learning techniques have
led to significant development in 2D and 3D human pose estimation
from RGB cameras, LiDAR, and radars. However, human pose esti-
mation from images is adversely affected by occlusion and lighting,
which are common in many scenarios of interest. Radar and LiDAR
technologies, on the other hand, need specialized hardware that is
expensive and power-intensive. Furthermore, placing these sensors
in non-public areas raises significant privacy concerns.
To address these limitations, recent research has explored the use
of WiFi antennas (1D sensors) for body segmentation and key-point
body detection. This paper further expands on the use of the WiFi
signal in combination with deep learning architectures, commonly
used in computer vision, to estimate dense human pose correspon-
dence. We developed a deep neural network that maps the phase
and amplitude of WiFi signals to UV coordinates within 24 human
regions. The results of the study reveal that our model can estimate
the dense pose of multiple subjects, with comparable performance
to image-based approaches, by utilizing WiFi signals as the only
input. This paves the way for low-cost, broadly accessible, and
privacy-preserving algorithms for human sensing.
Densepose

McDonald's AI Drive-Thru debacle is a warning to us all
By Joe Foley published 5 hours ago
Did it not test this?

We've mentioned before the risks for brands jumping on the AI bandwagon too quickly. And that extends beyond using AI image generators to any kind of customer-facing application, as McDonald's may have learned from its AI Drive Thru fiasco.
AI technology is advancing rapidly but remains in a state of relative infancy, and in many cases it just isn't good enough yet to implement without causing significant friction. The world's biggest fastfood brand has sensibly decided not to extend the contract on an AI voice recognition service and has told franchisees to remove the tech, but did it not think it should at least test it before it became the subject of viral videos?
Developed by IBM, McDonald's AI ordering system was implemented in over 100 McDonald's locations in the US starting back 2021. It was supposed to use voice recognition to process orders, but customers reported frequent frustrations, including quite spectacular order mixups, from bacon being added to ice cream to orders being hugely inflated.
In one video shared on TikTok with the caption "Fighting with McDonald's robot", the AI interpreted a woman's request for vanilla ice cream and a bottle of water to be an order for a caramel sundae and multiple sachets of ketchup and butter. In another, a customer inadvertently ordered 2,510 McNuggets Meals. That left a human attendant to have to reinput the order, rendering the AI a pointless frustration.
As reported by the trade publication Restaurant Business, McDonald's is removing the tech but remains determined to push forward with voice recognition technology to avoid having to employ humans to do the job of taking orders. The company said in a statement: "While there have been successes to date, we feel there is an opportunity to explore voice ordering solutions more broadly.
"After a thoughtful review, McDonald's has decided to end our current partnership with IBM on AOT (automated order taking) and the technology will be shut off in all restaurants currently testing it no later than 26 July, 2024."
This is far from the first case we've seen of experiments with AI resulting in a customer backlash. Lego is one of several brands to have apologised after using AI imagery. We've also seen branding agencies warn against AI washing, which is a tendency for companies to overstate their AI capabilities in order to make themselves look like part of the zeitgeist.

L’effondrement de l’information ?

Depuis Cambridge Analytica, Trump, le Brexit et le Covid, l’information est devenue un problème pour les réseaux sociaux… Sommés par les autorités d’arbitrer la vérité, la plupart d’entre eux semblent désormais se réfugier en-dehors de l’information, pour devenir des lieux d’accomplissement de soi rétifs à la politique. C’est certainement ce qui explique le recul de l’information dans les flux des utilisateurs, analyse pertinemment Charlie Warzel pour The Atlantic. Comme le déclarait récemment le New York Times : « Les principales plateformes en ligne sont en train de rompre avec l’information ».
Les plateformes de réseaux sociaux ont longtemps influencé la distribution de l’information, par exemple, en poussant les médias à se tourner vers la vidéo, comme l’a fait Facebook en 2015, en surestimant volontairement le temps moyen que les utilisateurs passaient à regarder des vidéos pour pousser les médias à basculer vers la production de contenus vidéos. Aujourd’hui, elles se détournent de l’information pour le divertissement et la publicité. Mais il n’y a pas qu’elles, les lecteurs eux-mêmes semblent atteindre un plafond informationnel, qui les pousse à se détourner de l’info, rapporte le Pew Research Center. La consommation d’information, particulièrement anxiogène, a plongé depuis 2020. Beaucoup se sont tournés vers des contenus plus faciles, comme ceux produits par les influenceurs. “La confiance des consommateurs ne repose pas nécessairement sur la qualité du reportage ou sur le prestige et l’histoire de la marque, mais sur des relations parasociales fortes”, constate Warzel. En 2014 – l’époque faste de l’actualité sociale – 75 % des adultes américains interrogés par le Pew déclaraient qu’Internet et les médias sociaux les avaient aidés à se sentir plus informés. Ce n’est plus le cas.
Avec l’accélération algorithmique de l’information dans les réseaux sociaux, les cycles d’actualité sont devenus plus rapides : Twitter est ainsi devenu le rédacteur en chef des sujets les plus chauds que les médias devaient traiter, dans une boucle de renforcement des sujets populaires, à l’image des tweets de Donald Trump que tous les médias commentaient. De 2013 à 2017, l’actualité est devenue l’essence faisant tourner les réseaux sociaux, transformant peu à peu l’information en champ de bataille… Beaucoup d’utilisateurs s’en sont alors détournés. De nouveaux réseaux sociaux ont explosé, à l’image de TikTok et les plus anciens réseaux se sont adaptés, Facebook notamment… Une récente enquête de Morning Consult a montré que « les gens aimaient davantage Facebook maintenant qu’il y avait moins d’actualité ».
Les commentaires sur l’actualité comme l’information ne vont pas entièrement disparaître, estime Warzel, mais les médias viennent de perdre de leur influence culturelle. Pour John Herrman dans le New Yorker, la campagne présidentielle de 2024 aux Etats-Unis risque d’être la première sans médias pour façonner les grands récits politiques. “Les réseaux sociaux ont fait ressortir le pire dans le secteur de l’information, et les informations, à leur tour, ont fait ressortir le pire dans de nombreux réseaux sociaux”. L’alliance entre réseaux sociaux et information a vécu. Reste à savoir ce que le monde de l’influence va produire… dans un monde où la force de l’écrit et la structuration de l’information semblent s’estomper du fait de machines à recommandation qui ne sont plus bâties pour eux.
La fin d’un monde commun
Dans un second article, Warzel revient sur cette disparition de l’information… Pour lui, l’internet est désormais fragmenté par les recommandations sociales qui font que nous ne partageons pas grand-chose de ce que les autres consomment. “La notion même de popularité est sujette à débat” : plus personne ne sait vraiment si telle tendance est aussi virale qu’affichée. Difficultés à comparer les métriques, recommandations opaques, fermeture des sites d’information par les paywalls, chute de la pertinence des informations sur les médias sociaux et envahissement publicitaire… Nous ne comprenons plus ce qu’il se passe en ligne. Vous n’avez probablement jamais vu les vidéos les plus populaires de TikTok de l’année, pas plus que les contenus les plus vus de Facebook ! Et pas grand monde n’avait parlé de l’émission la plus populaire de Netflix, The Night Agent ! D’un côté, les contenus populaires sont plus viraux que jamais, de l’autre ces popularités sont plus cloisonnées que jamais ! Les comparaisons d’audience entre contenus et plateformes deviennent particulièrement complexes à décoder. Par exemple, la polémique récente sur le succès d’audience auprès de jeunes américains d’un discours de Ben Laden n’a pas été aussi virale que beaucoup l’ont dit, comme l’ont démontré le Washington Post ou Ryan Broderick. Un peu comme si nous étions entrés dans un moment de grande confusion sur la viralité, avec des métriques de vues que l’on compare d’une plateforme l’autre, alors que leurs publics et principes d’auto-renforcement sont très différents. Le fait que les plateformes ferment l’accès à leurs métriques et à la recherche n’aide pas à y voir clair, bien sûr. Sans échelle de comparaison, sans moyens pour voir ce qui circule et comment, nous devenons aveugles à tous les phénomènes. Et notamment à l’un d’entre eux : la manipulation de l’information par des puissances étrangères…

Ces transformations ne sont pas encore achevées ni digérées qu’une autre se profile, estimait James Vincent pour The Verge : “l’ancien web est en train de mourir et le nouveau web a du mal à naître”. La production de textes, d’images, de vidéos et de sons synthétiques vient parasiter cet écosystème en recomposition. Accessibles directement depuis les moteurs de recherches, les productions de l’IA viennent remplacer le trafic qui menait jusqu’à l’information. “L’IA vise à produire du contenu bon marché depuis le travail d’autrui”. Bing AI ou Bard de Google pourraient finalement venir tuer l’écosystème qui a fait la valeur des moteurs de recherche, en proposant eux-même leur propre “abondance artificielle”. Certes, ce ne sera pas la première fois que l’écosystème de l’information se modifie : Wikipédia a bien tué l’Encyclopédie Britannica. Mais, pour James Vincent, si depuis l’origine le web structure la grande bataille de l’information en modifiant les producteurs, les modalités d’accès et les modèles économiques… cette nouvelle configuration qui s’annonce ne garantit pas que le système qui arrive soit meilleur que celui que nous avions.
“L’internet n’est plus amusant”, déplorait Kyle Chayka pour le New Yorker. A force d’ajustements algorithmiques, les réseaux sociaux sont devenus parfaitement chiants !, expliquait Marie Turcan de Numérama, dénonçant le web de l’ennui ! L’invisibilisation des liens externes et plus encore de l’écrit par rapport à la vidéo, semble achever ce qu’il restait de qualité, comme le rapporte David-Julien Rahmil pour l’ADN. Dans un autre article, Rahmil rappelle que les échanges directs ont pris le pas sur les échanges publics : “La publicité omniprésente, l’exacerbation des tensions politiques, la culture du clash perpétuel et la sensation de burn-out informationnel ont sans doute précipité la chute des grandes plateformes sociales.” Désormais, chaque plateforme ne travaille plus que pour elle-même. Dans une internet plus fragmenté que jamais, chaque plateforme va faire émerger ses propres professionnels, ses propres influenceurs et il est bien probable qu’ils ne se recoupent plus d’une plateforme l’autre.

Quant aux réseaux sociaux, ils se sont dévalorisés eux-mêmes, à l’image de Twitter, qui a longtemps incarné le fil d’actualité en temps réel, le lieu central d’une conversation influente et un peu élitiste, explique Nilay Patel pour The Verge. C’est “l’effondrement du contexte qui a rendu Twitter si dangereux et si réducteur, mais c’était aussi ce qui le rendait passionnant”. La plateforme a rendu ses utilisateurs plus rapides et plus agiles, mais également trop réactifs. Les marques se sont éloignées des médias pour gérer elles-mêmes leurs présences sociales. “En prenant du recul maintenant, vous pouvez voir exactement à quel point cette situation a été destructrice pour le journalisme : les journalistes du monde entier ont fourni gratuitement à Twitter des informations et des commentaires en temps réel, apprenant de plus en plus à façonner des histoires pour l’algorithme plutôt que pour leurs véritables lecteurs. Pendant ce temps, les sociétés de médias pour lesquelles ils travaillaient étaient confrontées à un exode de leurs plus gros clients publicitaires vers des plateformes sociales offrant des produits publicitaires de meilleure qualité et plus intégrés, une connexion directe avec le public et aucune éthique éditoriale contraignante. Les informations sont devenues de plus en plus petites, même si les histoires ont pris de l’ampleur.” Tout le monde y était journaliste, alors que le secteur de l’information lui-même se tarissait. “Twitter a été fondé en 2006. Depuis cette année-là, l’emploi dans les journaux a chuté de 70% et les habitants de plus de la moitié des comtés américains ont peu ou plus d’informations locales”. Avec la pandémie, Trump, Black Live Matter, Twitter a atteint un point de bascule, s’effondrant sous son propre pouvoir. L’audience a commencé à refluer sous sa toxicité. Pour Patel, la prise de pouvoir de Musk sur la plateforme est une réaction au recul du pouvoir des célébrités et des gens de la tech. En renforçant sa viralité et sa toxicité, la plateforme ne cesse de péricliter. Les challengers (Bluesky, Threads, Mastodon…) sont à Twitter “ce que la méthadone est à l’héroïne”. L’audience est plus fragmentée que jamais. A l’image de ces utilisateurs qui courent encore d’une plateforme l’autre pour envoyer des messages à leurs relations… ou ces lecteurs désorientés de ne plus trouver quoi lire.
Changement générationel ou enjunkification ?**
**L’âge de la conversation qui ouvrait le web du XXIe siècle est clos ! Et ce qu’il reste de nos conversations vont être prises en charge par des agents conversationnels… qui seront des des agents politiques et idéologiques bien plus efficaces que nos semblables, comme l’explique Olivier Ertzscheid ! A terme, c’est même une relation encore plus personnelle à l’information que dessinent les chatbots, chacun discutant avec le sien sans plus vraiment avoir de liens à des contenus communs.

Pour Max Read, dans le New York Times, peut-être faut-il lire ces changements en cours autrement. Ces transformations ont aussi des origines économiques, rappelle-t-il trop rapidement. “La fin de l’ère des taux d’intérêt bas a bouleversé l’économie des start-ups, mettant fin aux pratiques de croissance rapide comme le blitzscaling et réduisant le nombre de nouvelles entreprises Internet en lice pour attirer notre attention ; des entreprises comme Alphabet et Facebook sont désormais des entreprises matures et dominantes au lieu de nouvelles entreprises perturbatrices”… Pourtant, plutôt que de creuser cette explication économique, c’est à une autre explication que Max Read se range. Si l’internet est en train de mourir, c’est d’abord parce que nous vieillissons. La forme et la culture d’internet ont été façonnés par les préférences des générations qui y ont pris part. L’internet d’aujourd’hui n’est plus celui des médias sociaux (2000-2010), ni celui des réseaux sociaux (2010-2020). “Selon le cabinet d’études de consommation GWI, le temps passé devant un écran par les millennials est en baisse constante depuis des années. Seuls 42 % des 30 à 49 ans déclarent être en ligne « presque constamment », contre 49 % des 18 à 29 ans. Nous ne sommes même plus les premiers à l’adopter : les 18 à 29 ans sont plus susceptibles d’avoir utilisé ChatGPT que les 30 à 49 ans – mais peut-être uniquement parce que nous n’avons plus de devoirs à faire.”
“Le public américain le plus engagé sur Internet ne sont plus les millennials mais nos successeurs de la génération Z. Si Internet n’est plus amusant pour les millennials, c’est peut-être simplement parce que ce n’est plus notre Internet. Il appartient désormais aux zoomers.”
Les formats, les célébrités, le langage lui-même de cette génération est totalement différent, explique Read. “Les zoomers et les adolescents de la génération Alpha qui mordillent leurs talons générationnels semblent toujours s’amuser en ligne. Même si je trouve tout cela impénétrable et un peu irritant, l’expression créative et la socialité exubérante qui ont rendu Internet si amusant pour moi il y a dix ans sont en plein essor parmi les jeunes de 20 ans sur TikTok, Instagram, Discord, Twitch et même X. Skibidi Toilet, Taxe Fanum, le rizzler – je ne me rabaisserai pas en prétendant savoir ce que sont ces mèmes, ou quel est leur attrait, mais je sais que les zoomers semblent les aimer. Ou, en tout cas, je peux vérifier qu’ils adorent les utiliser pour confondre et aliéner les millennials d’âge moyen comme moi.”
Certes, ils sont récupérés et exploités par une petite poignée de plateformes puissantes, mais d’autres avant elles ont cherché à arbitrer et à marchandiser notre activité en ligne… “Les plateformes axées sur l’engagement ont toujours cultivé les influenceurs, les abus et la désinformation. Lorsque vous approfondissez, ce qui semble avoir changé sur le Web au cours des dernières années, ce n’est pas la dynamique structurelle mais les signifiants culturels”.
“En d’autres termes, l’enjunkification a toujours eu lieu sur le web commercial, dont le modèle économique largement basé sur la publicité semble imposer une course toujours mouvante vers le bas. Peut-être que ce que les internautes frustrés, aliénés et vieillissants comme moi vivent ici, ce ne sont pas seulement les fruits d’un Internet enjunkifié, mais aussi la perte de l’élasticité cognitive, du sens de l’humour et de l’abondance de temps libre nécessaire pour naviguer avec agilité et gaieté dans tous ces déchets déroutants.”
Mais c’est là une vision très pessimiste des transformations actuelles. Pour Rolling Stone, Anil Dash s’enthousiasme. Avec sa fragmentation, l’internet est en train de redevenir bizarre, comme il l’était à l’origine ! La disparition d’applications centrales (même si ce n’est pas vraiment tout à fait le cas), promet un retour de services étranges et de propositions inattendues à l’image de l’école de la programmation poétique de Neta Bomani… ou celles du constructeur de bots Stephan Bohacek, ou encore celles du designer Elan Kiderman Ullendorff qui s’amuse à faire des propositions pour “échapper aux algorithmes“… ou encore les petites subversions de l’artiste et programmeur Darius Kazemi qui proposait aux gens de créer leurs micro-réseaux sociaux autonomes sur Mastodon…
Pas sûr que ces subversions n’aient jamais cessé. Elles ont surtout été invisibilisées par les grandes plateformes sociales. Pas sûr que l’audience d’influence et que l’audience synthétique qui s’annoncent ne leur apporte plus d’espaces qu’ils n’en avaient hier. Reste qu’Anil Dash a raison : la seule chose certaine, c’est que les contenus les plus étranges vont continuer de tenter de parvenir jusqu’à nous. A l’image des vidéos qui venaient coloniser les flux des plus jeunes depuis quelques mots clefs, que dénonçait James Bridle dans son excellent livre, Un nouvel âge des ténèbres. Elan Kiderman Ullendorff s’est amusé à créer un compte tiktok des vidéos les plus repoussantes qui lui étaient proposées en passant toutes celles qui l’intéressaient et en ne retenant que le pire. Des vidéos qui semblent composer un portrait de Dorian Gray de chacun d’entre nous. Le web addictif est le miroir du web répulsif, le web qu’on déteste le miroir du web de nos rêves. Seule certitude, oui : le web de demain risque d’être bien plus étrange et dérangeant qu’il n’est ! Les ajustements algorithmiques ayant sabré le plus intéressant, il est probable que nous soyons plus que jamais confrontés au pire !
Hubert Guillaud

Social Media Messed Up Our Kids. Now It Is Making Us Ungovernable.
Jonathan Haidt talks to Noema about “The Anxious Generation” and how technology is upending democracy.
InterviewDigital Society June 13, 2024
In a conversation with Noema editor-in-chief Nathan Gardels, the social psychologist Jonathan Haidt discusses the impact of social media on truth in politics, the mental health crisis of today’s youth, and what to do about it.
Nathan Gardels: For those who haven’t read your book, “The Anxious Generation,” can you summarize the main thesis?
Jonathan Haidt: It all begins with a mystery: Why is it that mental health statistics for American teenagers were pretty flat, with no sign of any problem, from the late ’90s through 2010 to 2011? That is true whether we look at depression, anxiety or self-harm. And then, all of a sudden, in 2012, it’s as though someone flipped a switch, and the girls began getting much more anxious, depressed and self-harming. It was true of boys too, but it’s not been so sudden. It was more gradual in the early 2010s.
We first discovered this on college campuses because the students who entered universities from 2014 to 2015 were very different from our stereotype of college students who want to have fun, who want to drink and party.
The students arriving in 2014 to 15 were much more anxious. And they were especially triggered by words or jokes, speakers or books. It was that observation that led Greg Lukianoff to propose the hypothesis that college is doing something to kids to make them think in this distorted way. That was the basis of our book “The Coddling of the American Mind.”
But now it’s becoming clearer that what we saw and wrote about in that book wasn’t just happening to college students, but actually to all teenagers born after 1995. And it was not only observable in the U.S., Britain and Canada but a lot of other countries as well. What happened? Why was it so sudden? So that’s the mystery.
Was it some chemical dropped in the water supply all over North America and Northern Europe, along with the South Pacific? Or was it the massive change in the technological environment of childhood in all these countries simultaneously? This seemed the obvious hypothesis.
So, the first chapter of “The Anxious Generation” discusses what actually happened to teen mental health. And then the rest of the book seeks to unravel the mystery. It’s not just about “social media is destroying everybody.” It’s a more subtle and interesting story about the transformation of childhood — a tragedy that occurred in three acts.
Act I, which I only hinted at in the book, was the loss of community. So, if you look at America, especially in the years just after World War II, social capital was very high. The best way to make people trust each other is to have someone attack them from the outside — come together, fight a war and win. Social capital was very high in the U.S. in the 1940s and 1950s, and then it begins to drop over succeeding decades for many reasons.
Robert Putnam talked about this in “Bowling Alone.” You have smaller family sizes; people retreat inside because now they have air conditioning and TV and they’re not out in the front yard socializing as much. So, for a lot of reasons, we begin to lose trust in each other. We begin to lose social capital. That’s Act I of the tragedy.
Because of that, Act II happens, which is when we take away play-based childhood. Children used to always play together. It didn’t matter if it was raining or snowing, if there was a crime wave or drunk drivers, kids went out to play. Like all mammals, we evolved to play, in order to wire up our relatively large brains.
But in the ’90s, we decided it was too dangerous for kids to be out and about. They’ll get kidnapped or sexually abused, we thought, because we no longer trusted our neighbors. So, we locked our kids up out of fear of each other. In other words, over protection. This is the coddling part.
Then, after losing strong communities and play-based childhoods, we’re ready for the third act in the tragedy: the massive, sudden transformation of childhood between 2010 and 2015 into a phone-based childhood.
In 2010, the vast majority of teens across the developed world had cell phones. But they were flip phones or basic phones, with no internet browser. All you could do with them is text and call. That was pretty much it aside from some games. It wasn’t for constant communication. And that’s good. Kids could text their friends and say, “Let’s meet up at 3 p.m.” It was a simple tool. There was very little high-speed internet then and no front-facing camera. There was Facebook, but no Instagram. That’s the way things were in 2010.
“All of a sudden, in 2012, it’s as though someone flipped a switch, and the girls began getting much more anxious, depressed and self-harming.”
In 2010, kids in the U.S. and other Anglo countries still had a recognizably human childhood. They would meet up in person, even if they now had less freedom to roam. By 2015, that all changed when about 80% of those kids had a smartphone with a front-facing camera and a bunch of social media apps. So now we have the selfie culture. Almost everyone now has high-speed internet and now everyone can display video.
In short, by 2015 we have what I call “the great rewiring of childhood.” And that’s why in 2012, which is the year, incidentally, that Facebook bought Instagram, when online life changed, especially for girls, who flocked onto Instagram. And it was right after that when we first noticed the widespread upsurge in anxiety, depression and self-harm.
Gardels: The main criticism of your thesis is that you are mistaking correlation for cause and being too technologically determinist. How do you respond to that?
Haidt: First of all, my story is not just about technology, it is sociological. It’s a cultural psychology story. It’s about the change of childhood and human development.
To those who argue these changes could have been caused by any number of factors, I say a couple of things. First, whatever other factor you might think was more determinative, did that happen in New Zealand and Iceland and Australia all at the same time? No one can identify such a factor. Nobody has proposed an alternative theory that works internationally.
Second, it is true that the data is mostly correlational. If you have 300 correlational studies and 25 experimental studies, I would say the data is mostly correlational. The scientific debate has been focused on a very, very narrow question: Do the hours spent on social media tell you anything about the level of mental illness, especially depression and anxiety? There’s a clear correlation in these studies.
But we also have experimental studies, which I cite in the book. I go into great detail about the difference between correlation and causation. Every week, every month, we have more experiments indicating the causality of anxiety-inducing technology.
There are so many causal pathways by which a phone-based childhood harms different kids in different ways. Let me just take the example of sextortion, a very common crime online. There are international sextortion gangs that display avatars of beautiful, sexy young women. An avatar flirts with a boy that she finds, usually on Instagram. And then she convinces him to swap nude images. Boom. Then the sextortionist reveals himself, not as a sexy girl but as a man who now has all the content he needs to ruin you: “I’m going to show this picture of you and your penis to everyone, because I have all your contacts, unless you pay me $500 in two hours.”
The boys panic, and some of them have killed themselves because of the shame. The FBI has identified 20 suicides that were direct results of sextortion, which means there are probably hundreds of cases they didn’t catch, and far more kids who were traumatized by the experience and the shame. Now, is that just a correlation? Would these boys have killed themselves anyway, even if they had not been sextorted? I don’t think so.
Gardels: What are the specific remedies you propose for parents to protect their kids?
Haidt: The key to the whole book is understanding collective action problems, which are sometimes referred to as “the tragedy of the commons,” where each person acting in their own interest ends up bringing about an outcome that’s bad for everyone. If you’re the only one who doesn’t put your sheep out to graze, if you’re the only one who doesn’t fish in the pond, you suffer while everyone else continues to do what they’re doing.
One of the main reasons that we all are giving our kids phones now at age nine or 10 — it gets younger all the time — is because the kid comes home from school and says, “Mom, everyone else has an iPhone, I have to have an iPhone, or I’ll be left out.”
This is a collective action problem because any parent who does the right thing and says, “No, you’re not going to get one until you’re mostly done with puberty,” is imposing a cost on their child. All over the developed world now, family life has devolved into a struggle over screen time and phones. This is terrible. So, the trick is to realize we’re in this problem because everybody else is in this problem.
“All over the developed world now, family life has devolved into a struggle over screen time and phones.”
We’re so deep into this that it is very hard for any family to get out of it by themselves. Some parents are tough and just say “no,” but the status environment doesn’t change for the kids.
What I’m trying to do with the book is to say, if we team up with a few other families, if a small group of parents can get the whole school or school district to say “no,” then they escape and we can change the situation very, very quickly.
What we need is the adoption of four norms that can break the back of the collective action problem.
One: No smartphone before high school. Just keep it out of middle school. Let the kids at least get through early puberty, which is the most sensitive period. You can give them a flip phone if you absolutely need to text. I understand the need to coordinate.
Two: No social media before the age of 16. Social media is entirely inappropriate for children, it cannot be made appropriate because what you’re basically doing is saying, “How about we let the entire world get in touch with you? Let’s let all the companies try to sell things to you, let men all over the world who want to have sex with you contact you, and try to trick you into sending photos.” There’s no way to make this safe. So just recognize that social media is a tool for adults. Eleven-year-olds don’t need to network with strangers.
Third: Schools need to be phone-free. Imagine that when I was a kid growing up in the ’70s, if we had been allowed to bring in our television sets and our radios along with all sorts of toys and games and put them on our desk and use them during class. That’s what teachers are facing today. Disgusted and frustrated that they can’t get through to students, teachers are quitting.
Also, global test scores have been dropping, since 2012. This did not begin with Covid. It began around 2012. The result is a massive destruction of human capital. So, it’s just kind of obvious. You can’t have kids have the greatest distraction device ever invented in their pockets while they’re in class. All kids must check their phones during the day. If others are texting, they have to be texting back. So, just lock up the phone in the morning to give it back at the end of the day.
Four: We need to restore a play-based childhood. Kids need more independence, free play and responsibility in the real world. If you’re going to roll back the phone and don’t restore play, a child can have no childhood. So, roll it back and instead, give them adventure and fun with other kids.
Us parents need to overcome our own fears and let our children learn how to play with each other. Kids playing in groups are very safe. That’s how they learn to get along. That’s how they’re going to resolve disputes in life.
If we do these four things I’m pretty confident that rates of mental illness will come down within two years. Experience so far shows that phone-free schools get great results within a month. In various childhood independence projects, you get results within a month. If any community does all four of these, I believe they’re going to see pretty big drops in depression, anxiety, self-harm and other problems in short order.
Gardels: Do you worry that more prosperous parents with the means and time to be attentive to their kids will follow your advice, while the less well-off, busy working two jobs with less time for their kids, won’t? That this will just create a greater gap in society?
Haidt: Yes, I do expect that it will begin this way, with the most educated and wealthy families. But I think it will spread quickly as parents begin to see and hear about the benefits. Also, I should note that the most educated families apply the most limits, whereas children in low socioeconomic status, single-parent, or Black or Hispanic families have one- to two- hours more screen time per day, so going phone-free will disproportionately help them.
Gardels: Implicit in your remarks is you don’t have any faith in the Instagrams or TikToks of the world to be able to regulate themselves so they do less harm?
“What we need is the adoption of four norms that can break the back of the collective action problem.”
Haidt: Right now, as long as you’re old enough to lie about your age, you can go to Pornhub. You can open 20 Instagram accounts, you can open TikTok accounts. The law says you have to be 13 to sign a contract with a company to give away your data without your parents’ knowledge. But the law is written in such a way that there’s no responsibility for the companies if they don’t know your real age. As long as they don’t know your real age, they can’t be held liable for serving you eating disorder content or sex and violence.
We’re talking about five to 10 companies here that own our children’s childhood. They have a lot more influence over our kids than we do in some ways. And they have no responsibility. They are literally protected from lawsuits by Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, which shields them from liability for the content on their platforms.
This is a completely insane situation. And they’re making huge amounts of money. So no, I don’t expect them to do anything until they’re forced by legislation, or by enormous losses in court.
Gardels: Your book has obviously hit a chord with parents and with school authorities. Do you have any sense of how the TikTok crowd or kids themselves see it?
Haidt: When you survey kids who’ve been through this, it’s really hard to find members of Gen Z who are opposed to what I’m saying. In fact, I actually haven’t found any. They almost always say, “Yeah, you know, you’re right. This really messed us up. But, you know, what are you going to do? This is just the way things are, and I can’t quit because everyone else is on.” There’s just an extraordinary sense of fatalism. We don’t find any young people organizing to protect their rights to have these things. The older kids generally say, if we could get everyone off, we should do that.
Gardels: The Chinese cyberspace authorities have no qualms about imposing limits on social media. Here are the rules:
- Children under 8: Can only use smart devices for 40 minutes per day and can only consume content about “elementary education, hobbies and interests, and liberal arts education”
- Children aged 8 to 15: Can use their phone for no more than one hour per day
- Children aged 16 to 17: Can use a handset for a maximum of two hours per day
- Minor mode: Requires mobile devices, apps and app stores to have a built-in mode that would bar users under 18 from accessing the internet on mobile devices from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m.
Perhaps they will produce more mentally healthy kids?
Haidt: China is engaged in a battle with the United States for cultural and economic supremacy. Since our young people are giving away all of their available attention, there’s a good chance that they will be less creative and less productive. They don’t have any spare attention to actually do anything. I imagine that makes the Chinese government happy.
The worst single product for American children is TikTok. It sucks up more of their time, energy and attention than any other product. And it harms them. It doesn’t do anything good for them. TikTok has more influence over our kids than any other organization on the planet. So, there are many reasons to think that that is a danger not only to our kids, but to our country.
It seems the Chinese are doing the right thing by using their authoritarian system to reduce the damage to their own children.
Of course, authoritarian solutions are not right for us, but we can do similar things through democratic solutions, through community and civil society. One thing Tocqueville praised Americans about is that when something needs doing, say the townspeople need to build a bridge, they just do it. They don’t wait for the state like in France. They don’t wait for the King like in Britain. Americans come together as citizens, elect a leader, raise money and then they do it.
So, I’m hopeful that my book presents norms that we adopt ourselves, even if we never get any help from Congress or lawmakers. Doing it ourselves — in groups of parents organized around schools — is a very American solution to what I think is one of the largest problems facing America today.
“TikTok has more influence over our kids than any other organization on the planet.”
Gardels: To go back to the coddled generation argument. What do you make of all these kids in college today putting up barricades, occupying administration buildings protesting the war in Gaza?
Haidt: Most of the activism of the college kids has moved online. That tends to be very ineffective and creates a culture that is bad for activists. I put some research in the book showing that before 2010, being politically active was actually associated with better mental health. You were engaged, you were part of a group, you were energized. After 2010, activists, especially progressive activists, are the least happy people in the country. They are marinating in beliefs about oppressor versus victim and embracing the untruths of the coddled. That was certainly true until very recently.
Now it’s true these protests are in person. That’s at least better psychologically for them. They are physically present and interacting with others on campus.
Even so, I think there are signs that it’s different from previous generations. One is that the present protestors are expecting accommodation, often seeking not to be punished for missing classes and for delayed exams. In other words, they are expecting a low cost to themselves. In previous periods of activism, civil disobedience meant if you break the law, then you pay the consequences to show how committed you are to the cause.
To be sure, today’s actions are communal, which is always very exciting. It’s not as though Gen Z is incapable of acting in person; though, I would point out, it’s overwhelmingly at the elite schools that this is happening.
Gardels: One of the reasons that we have such a paralyzed and polarized society is that the public square has virtually disappeared. Until social media turbocharged fragmentation, there was a common space where competing ideas could be contested in the full gaze of the body politic.
As the philosopher Byung-Chul Han has observed, the peer-to-peer connectivity of social media redirects the flow of communication. Information is spread without forming a public sphere. It is produced in private spaces and distributed to private spaces. The web does not create a public.
The possibility of arriving at a governing consensus through negotiation and compromise is being shattered by a cacophony of niche propagandists egging on their own siloed tribe of the faithful to engage in an endless partisan battle. Indeed, Rene DiResta at Stanford calls the niche ideologues “the new media goliaths” who have supplanted mainstream platforms in terms of influence.
In short, the digital media ecosystem is disempowering the public sphere.
In this sense, social media is not only messing up our kids but undermining the basis of democratic discourse.
Do you agree with that?
Haidt: Absolutely. In an article for the Atlantic in 2019, I made the case, basically along the lines of Han, that massive changes in information flows and the way we connect people change the fundamental ground within which our democratic institutions are operating. And it’s quite possible that we are now so far outside the operating range of these institutions that they will fail.
I’m extremely alarmed about the future of this country. If you read Federalist #10, the Founding Fathers, who were excellent social psychologists, were very afraid of the passions of the people. They didn’t want us to have a direct democracy. They wanted cooling mechanisms of deliberation through reason. The system of governance they devised, with its checks and balances, is really like a complicated clock that they thought could last a very long time precisely because it was realistic about human frailties. And they were right.
Then all of a sudden in the later post-war era — first with television, then the internet and, especially, now peer-to-peer media, it is all going awry. With television, at least there were editors. Jonathan Rauch wrote an amazing book called “The Constitution of Knowledge,” both about the Constitution and how knowledge is constituted.
He discussed how we make knowledge in universities and science and medicine. But he also discussed the U.S. Constitution and how the community of knowledge makers are governed by certain rules and checks and balances. We developed editors, filters and other mechanisms to vet truth.
All that’s going away now. Or at least the institutions are so weakened as to be feeble. I’m very alarmed. And, at the same time, what’s replacing them are the sorts of peer-to-peer networks that you’re talking about.
“Until social media turbocharged fragmentation, there was a common space where competing ideas could be contested in the full gaze of the body politic.”
In the history of humanity, when you connect people, there could be disruptions. But in the long run, that’s good. It increases the flow of knowledge and increases creativity. You get more value when you connect people. So, the telephone was great, the postal system was great.
Social media is not like those earlier innovations. I think the best metaphor here is to imagine a public square in which people talk to each other. They debate ideas or put forth ideas that may not always be brilliant. They may not always be civil, but people can speak while others listen. Sometimes people are moved by persuasion or dissuasion.
I think the Founding Fathers assumed that’s about the best we can hope for. Imagine one day, and I’ll call it 2009, that all changes. There’s no more public square. Everything takes place in the center of the Roman Colosseum. The stands are full of people who are there to see blood. That’s what they came for. They don’t want to see the lion and the Christian making nice; they want the one to kill the other. That’s what Twitter is often like.
It all becomes performative and comes at a superfast pace. Just as television changed the way we are and made us into passive consumers, the central act in social media is posting, judging, criticizing and joining mobs. Donald Trump is the quintessential person who thrives in that environment. If not for Twitter, Trump never could have been president. So, when our politics moved into the Roman Colosseum, I think the Founding Fathers would have said, “Let’s just give up. There’s no way we can build a democracy in this environment.”
Gardels: Just as republics have historically created institutional checks and balances when too much power is concentrated in one place, so too don’t we need to foster checks and balances for an age when power is so distributed that the public sphere is disempowered?
What I have in mind are the citizens’ assemblies indicative of the public as a whole, which deliberate issues in a non-partisan environment and, outside the electoral sphere where partisans vie for power by any means necessary, are able to come to a consensus through pragmatic, common sense solutions?
Haidt: It’s possible to create these small artificial communities where you lock citizens away together for a week and have them discuss something. They work pretty well from what I know, and they come up with solutions. But it’s not clear to me how you could use that to run a country. The way people feel about let’s say, Donald Trump, has very little to do with some ascertainment of fact.
If you use the word power, then I’m a little bit confused. But I think I see what you’re getting at. If we change the word to authority, it is clearer to me. When I wrote “The Righteous Mind,” I was on the left then and really tried to understand conservatives. Reading conservative writings, especially Edmund Burke and Thomas Sowell, was really clarifying on the idea that we need institutions. We need religion, we need gods, even if it is not true. We need moral order and constraint.
The progressive impulse is to tear things down and make things new. The conservative impulse is to protect authority structures because we need them. Without them, we have chaos. Of course, there are times to tear things down. But I think during the 2010s everything has been torn down, to some extent. This is a time we need to build.
I am very concerned that there is no longer any source of authority. There is no trusted authority, there is no way to find consensus on truth. It seems that the truth-seeking mechanisms, including the courts, came up with the answer that the last presidential election in the U.S. was not stolen. But there’s no real way to spread that around to the large portion of society that believes that it was.
With AI coming in, the problem of the loss of authority is going to be magnified tenfold or even a hundredfold when anyone can create a video of anyone saying anything in that person’s voice. It’s going to be almost impossible to know what’s true. We’re in for a wild ride if we’re going to try to run a democratic republic with no real authority. My fear is that we will simply become ungovernable. I hope not, I hope we find a way to adapt to living in our world after the fall of the tower of Babel, the fall of common understandings and common language.
This interview was edited for brevity and clarity.
Pentagon ran secret anti-vax campaign to undermine China during pandemic
The U.S. military launched a clandestine program amid the COVID crisis to discredit China’s Sinovac inoculation – payback for Beijing’s efforts to blame Washington for the pandemic. One target: the Filipino public. Health experts say the gambit was indefensible and put innocent lives at risk.
By CHRIS BING and JOEL SCHECTMAN Filed June 14, 2024, 9:45 a.m. GMT
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. military launched a secret campaign to counter what it perceived as China’s growing influence in the Philippines, a nation hit especially hard by the deadly virus.
The clandestine operation has not been previously reported. It aimed to sow doubt about the safety and efficacy of vaccines and other life-saving aid that was being supplied by China, a Reuters investigation found. Through phony internet accounts meant to impersonate Filipinos, the military’s propaganda efforts morphed into an anti-vax campaign. Social media posts decried the quality of face masks, test kits and the first vaccine that would become available in the Philippines – China’s Sinovac inoculation.
Reuters identified at least 300 accounts on X, formerly Twitter, that matched descriptions shared by former U.S. military officials familiar with the Philippines operation. Almost all were created in the summer of 2020 and centered on the slogan #Chinaangvirus – Tagalog for China is the virus.
“COVID came from China and the VACCINE also came from China, don’t trust China!” one typical tweet from July 2020 read in Tagalog. The words were next to a photo of a syringe beside a Chinese flag and a soaring chart of infections. Another post read: “From China – PPE, Face Mask, Vaccine: FAKE. But the Coronavirus is real.”
After Reuters asked X about the accounts, the social media company removed the profiles, determining they were part of a coordinated bot campaign based on activity patterns and internal data.
The U.S. military’s anti-vax effort began in the spring of 2020 and expanded beyond Southeast Asia before it was terminated in mid-2021, Reuters determined. Tailoring the propaganda campaign to local audiences across Central Asia and the Middle East, the Pentagon used a combination of fake social media accounts on multiple platforms to spread fear of China’s vaccines among Muslims at a time when the virus was killing tens of thousands of people each day. A key part of the strategy: amplify the disputed contention that, because vaccines sometimes contain pork gelatin, China’s shots could be considered forbidden under Islamic law.
The military program started under former President Donald Trump and continued months into Joe Biden’s presidency, Reuters found – even after alarmed social media executives warned the new administration that the Pentagon had been trafficking in COVID misinformation. The Biden White House issued an edict in spring 2021 banning the anti-vax effort, which also disparaged vaccines produced by other rivals, and the Pentagon initiated an internal review, Reuters found.
“I don’t think it’s defensible. I’m extremely dismayed, disappointed and disillusioned to hear that the U.S. government would do that.”
Daniel Lucey, infectious disease specialist at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine.
The U.S. military is prohibited from targeting Americans with propaganda, and Reuters found no evidence the Pentagon’s influence operation did so.
Spokespeople for Trump and Biden did not respond to requests for comment about the clandestine program.
A senior Defense Department official acknowledged the U.S. military engaged in secret propaganda to disparage China’s vaccine in the developing world, but the official declined to provide details.
A Pentagon spokeswoman said the U.S. military “uses a variety of platforms, including social media, to counter those malign influence attacks aimed at the U.S., allies, and partners.” She also noted that China had started a “disinformation campaign to falsely blame the United States for the spread of COVID-19.”
In an email, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs said that it has long maintained the U.S. government manipulates social media and spreads misinformation.
Manila’s embassy in Washington did not respond to Reuters inquiries, including whether it had been aware of the Pentagon operation. A spokesperson for the Philippines Department of Health, however, said the “findings by Reuters deserve to be investigated and heard by the appropriate authorities of the involved countries.” Some aide workers in the Philippines, when told of the U.S. military propaganda effort by Reuters, expressed outrage.
Briefed on the Pentagon’s secret anti-vax campaign by Reuters, some American public health experts also condemned the program, saying it put civilians in jeopardy for potential geopolitical gain. An operation meant to win hearts and minds endangered lives, they said.
“I don’t think it’s defensible,” said Daniel Lucey, an infectious disease specialist at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine. “I’m extremely dismayed, disappointed and disillusioned to hear that the U.S. government would do that,” said Lucey, a former military physician who assisted in the response to the 2001 anthrax attacks.
The effort to stoke fear about Chinese inoculations risked undermining overall public trust in government health initiatives, including U.S.-made vaccines that became available later, Lucey and others said. Although the Chinese vaccines were found to be less effective than the American-led shots by Pfizer and Moderna, all were approved by the World Health Organization. Sinovac did not respond to a Reuters request for comment.
Academic research published recently has shown that, when individuals develop skepticism toward a single vaccine, those doubts often lead to uncertainty about other inoculations. Lucey and other health experts say they saw such a scenario play out in Pakistan, where the Central Intelligence Agency used a fake hepatitis vaccination program in Abbottabad as cover to hunt for Osama bin Laden, the terrorist mastermind behind the attacks of September 11, 2001. Discovery of the ruse led to a backlash against an unrelated polio vaccination campaign, including attacks on healthcare workers, contributing to the reemergence of the deadly disease in the country.
“It should have been in our interest to get as much vaccine in people’s arms as possible,” said Greg Treverton, former chairman of the U.S. National Intelligence Council, which coordinates the analysis and strategy of Washington’s many spy agencies. What the Pentagon did, Treverton said, “crosses a line.”
‘We were desperate’
Together, the phony accounts used by the military had tens of thousands of followers during the program. Reuters could not determine how widely the anti-vax material and other Pentagon-planted disinformation was viewed, or to what extent the posts may have caused COVID deaths by dissuading people from getting vaccinated.
In the wake of the U.S. propaganda efforts, however, then-Philippines President Rodrigo Duterte had grown so dismayed by how few Filipinos were willing to be inoculated that he threatened to arrest people who refused vaccinations.
“You choose, vaccine or I will have you jailed,” a masked Duterte said in a televised address in June 2021. “There is a crisis in this country … I’m just exasperated by Filipinos not heeding the government.”
When he addressed the vaccination issue, the Philippines had among the worst inoculation rates in Southeast Asia. Only 2.1 million of its 114 million citizens were fully vaccinated – far short of the government’s target of 70 million. By the time Duterte spoke, COVID cases exceeded 1.3 million, and almost 24,000 Filipinos had died from the virus. The difficulty in vaccinating the population contributed to the worst death rate in the region.
A spokesperson for Duterte did not make the former president available for an interview.
Some Filipino healthcare professionals and former officials contacted by Reuters were shocked by the U.S. anti-vax effort, which they say exploited an already vulnerable citizenry. Public concerns about a Dengue fever vaccine, rolled out in the Philippines in 2016, had led to broad skepticism toward inoculations overall, said Lulu Bravo, executive director of the Philippine Foundation for Vaccination. The Pentagon campaign preyed on those fears.
“Why did you do it when people were dying? We were desperate,” said Dr. Nina Castillo-Carandang, a former adviser to the World Health Organization and Philippines government during the pandemic. “We don’t have our own vaccine capacity,” she noted, and the U.S. propaganda effort “contributed even more salt into the wound.”
The campaign also reinforced what one former health secretary called a longstanding suspicion of China, most recently because of aggressive behavior by Beijing in disputed areas of the South China Sea. Filipinos were unwilling to trust China’s Sinovac, which first became available in the country in March 2021, said Esperanza Cabral, who served as health secretary under President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo. Cabral said she had been unaware of the U.S. military’s secret operation.
“I’m sure that there are lots of people who died from COVID who did not need to die from COVID,” she said.
To implement the anti-vax campaign, the Defense Department overrode strong objections from top U.S. diplomats in Southeast Asia at the time, Reuters found. Sources involved in its planning and execution say the Pentagon, which ran the program through the military’s psychological operations center in Tampa, Florida, disregarded the collateral impact that such propaganda may have on innocent Filipinos.
“We weren’t looking at this from a public health perspective,” said a senior military officer involved in the program. “We were looking at how we could drag China through the mud.”
A new disinformation war
In uncovering the secret U.S. military operation, Reuters interviewed more than two dozen current and former U.S officials, military contractors, social media analysts and academic researchers. Reporters also reviewed Facebook, X and Instagram posts, technical data and documents about a set of fake social media accounts used by the U.S. military. Some were active for more than five years.
Clandestine psychological operations are among the government’s most highly sensitive programs. Knowledge of their existence is limited to a small group of people within U.S. intelligence and military agencies. Such programs are treated with special caution because their exposure could damage foreign alliances or escalate conflict with rivals.
Over the last decade, some U.S. national security officials have pushed for a return to the kind of aggressive clandestine propaganda operations against rivals that the United States’ wielded during the Cold War. Following the 2016 U.S. presidential election, in which Russia used a combination of hacks and leaks to influence voters, the calls to fight back grew louder inside Washington.
In 2019, Trump authorized the Central Intelligence Agency to launch a clandestine campaign on Chinese social media aimed at turning public opinion in China against its government, Reuters reported in March. As part of that effort, a small group of operatives used bogus online identities to spread disparaging narratives about Xi Jinping’s government.
COVID-19 galvanized the drive to wage psychological operations against China. One former senior Pentagon leader described the pandemic as a “bolt of energy” that finally ignited the long delayed counteroffensive against China’s influence war.
The Pentagon’s anti-vax propaganda came in response to China’s own efforts to spread false information about the origins of COVID. The virus first emerged in China in late 2019. But in March 2020, Chinese government officials claimed without evidence that the virus may have been first brought to China by an American service member who participated in an international military sports competition in Wuhan the previous year. Chinese officials also suggested that the virus may have originated in a U.S. Army research facility at Fort Detrick, Maryland. There’s no evidence for that assertion.
Mirroring Beijing’s public statements, Chinese intelligence operatives set up networks of fake social media accounts to promote the Fort Detrick conspiracy, according to a U.S. Justice Department complaint.
China’s messaging got Washington’s attention. Trump subsequently coined the term “China virus” as a response to Beijing’s accusation that the U.S. military exported COVID to Wuhan.
“That was false. And rather than having an argument, I said, ‘I have to call it where it came from,’” Trump said in a March 2020 news conference. “It did come from China.”
China’s Foreign Ministry said in an email that it opposed “actions to politicize the origins question and stigmatize China.” The ministry had no comment about the Justice Department’s complaint.
Beijing didn’t limit its global influence efforts to propaganda. It announced an ambitious COVID assistance program, which included sending masks, ventilators and its own vaccines – still being tested at the time – to struggling countries. In May 2020, Xi announced that the vaccine China was developing would be made available as a “global public good,” and would ensure “vaccine accessibility and affordability in developing countries.” Sinovac was the primary vaccine available in the Philippines for about a year until U.S.-made vaccines became more widely available there in early 2022.
Washington’s plan, called Operation Warp Speed, was different. It favored inoculating Americans first, and it placed no restrictions on what pharmaceutical companies could charge developing countries for the remaining vaccines not used by the United States. The deal allowed the companies to “play hardball” with developing countries, forcing them to accept high prices, said Lawrence Gostin, a professor of medicine at Georgetown University who has worked with the World Health Organization.
The deal “sucked most of the supply out of the global market,” Gostin said. “The United States took a very determined America First approach.”
To Washington’s alarm, China’s offers of assistance were tilting the geopolitical playing field across the developing world, including in the Philippines, where the government faced upwards of 100,000 infections in the early months of the pandemic.
The U.S. relationship with Manila had grown tense after the 2016 election of the bombastic Duterte. A staunch critic of the United States, he had threatened to cancel a key pact that allows the U.S. military to maintain legal jurisdiction over American troops stationed in the country.
Duterte said in a July 2020 speech he had made “a plea” to Xi that the Philippines be at the front of the line as China rolled out vaccines. He vowed in the same speech that the Philippines would no longer challenge Beijing’s aggressive expansion in the South China Sea, upending a key security understanding Manila had long held with Washington.
“China is claiming it. We are claiming it. China has the arms, we do not have it.” Duterte said. “So, it is simple as that.”
Days later, China’s foreign minister announced Beijing would grant Duterte’s plea for priority access to the vaccine, as part of a “new highlight in bilateral relations.”
China’s growing influence fueled efforts by U.S. military leaders to launch the secret propaganda operation Reuters uncovered.
“We didn’t do a good job sharing vaccines with partners,” a senior U.S. military officer directly involved in the campaign in Southeast Asia told Reuters. “So what was left to us was to throw shade on China’s.”
Military trumped diplomats
U.S. military leaders feared that China’s COVID diplomacy and propaganda could draw other Southeast Asian countries, such as Cambodia and Malaysia, closer to Beijing, furthering its regional ambitions.
A senior U.S. military commander responsible for Southeast Asia, Special Operations Command Pacific General Jonathan Braga, pressed his bosses in Washington to fight back in the so-called information space, according to three former Pentagon officials.
The commander initially wanted to punch back at Beijing in Southeast Asia. The goal: to ensure the region understood the origin of COVID while promoting skepticism toward what were then still-untested vaccines offered by a country that they said had lied continually since the start of the pandemic.
A spokesperson for Special Operations Command declined to comment.
At least six senior State Department officials responsible for the region objected to this approach. A health crisis was the wrong time to instill fear or anger through a psychological operation, or psyop, they argued during Zoom calls with the Pentagon.
“We’re stooping lower than the Chinese and we should not be doing that,” said a former senior State Department official for the region who fought against the military operation.
While the Pentagon saw Washington’s rapidly diminishing influence in the Philippines as a call to action, the withering partnership led American diplomats to plead for caution.
“The relationship is hanging from a thread,” another former senior U.S. diplomat recounted. “Is this the moment you want to do a psyop in the Philippines? Is it worth the risk?”
In the past, such opposition from the State Department might have proved fatal to the program. Previously in peacetime, the Pentagon needed approval of embassy officials before conducting psychological operations in a country, often hamstringing commanders seeking to quickly respond to Beijing’s messaging, three former Pentagon officials told Reuters.
But in 2019, before COVID surfaced in full force, then-Secretary of Defense Mark Esper signed a secret order that later paved the way for the launch of the U.S. military propaganda campaign. The order elevated the Pentagon’s competition with China and Russia to the priority of active combat, enabling commanders to sidestep the State Department when conducting psyops against those adversaries. The Pentagon spending bill passed by Congress that year also explicitly authorized the military to conduct clandestine influence operations against other countries, even “outside of areas of active hostilities.”
Esper, through a spokesperson, declined to comment. A State Department spokesperson referred questions to the Pentagon.
U.S. propaganda machine
In spring 2020, special-ops commander Braga turned to a cadre of psychological-warfare soldiers and contractors in Tampa to counter Beijing’s COVID efforts. Colleagues say Braga was a longtime advocate of increasing the use of propaganda operations in global competition. In trailers and squat buildings at a facility on Tampa’s MacDill Air Force Base, U.S. military personnel and contractors would use anonymous accounts on X, Facebook and other social media to spread what became an anti-vax message. The facility remains the Pentagon’s clandestine propaganda factory.
Psychological warfare has played a role in U.S. military operations for more than a hundred years, although it has changed in style and substance over time. So-called psyopers were best known following World War II for their supporting role in combat missions across Vietnam, Korea and Kuwait, often dropping leaflets to confuse the enemy or encourage their surrender.
After the al Qaeda attacks of 2001, the United States was fighting a borderless, shadowy enemy, and the Pentagon began to wage a more ambitious kind of psychological combat previously associated only with the CIA. The Pentagon set up front news outlets, paid off prominent local figures, and sometimes funded television soap operas in order to turn local populations against militant groups or Iranian-backed militias, former national security officials told Reuters.
Unlike earlier psyop missions, which sought specific tactical advantage on the battlefield, the post-9/11 operations hoped to create broader change in public opinion across entire regions.
By 2010, the military began using social media tools, leveraging phony accounts to spread messages of sympathetic local voices – themselves often secretly paid by the United States government. As time passed, a growing web of military and intelligence contractors built online news websites to pump U.S.-approved narratives into foreign countries. Today, the military employs a sprawling ecosystem of social media influencers, front groups and covertly placed digital advertisements to influence overseas audiences, according to current and former military officials.
China’s efforts to gain geopolitical clout from the pandemic gave Braga justification to launch the propaganda campaign that Reuters uncovered, sources said.
Pork in the vaccine?
By summer 2020, the military’s propaganda campaign moved into new territory and darker messaging, ultimately drawing the attention of social media executives.
In regions beyond Southeast Asia, senior officers in the U.S. Central Command, which oversees military operations across the Middle East and Central Asia, launched their own version of the COVID psyop, three former military officials told Reuters.
Although the Chinese vaccines were still months from release, controversy roiled the Muslim world over whether the vaccines contained pork gelatin and could be considered “haram,” or forbidden under Islamic law. Sinovac has said that the vaccine was “manufactured free of porcine materials.” Many Islamic religious authorities maintained that even if the vaccines did contain pork gelatin, they were still permissible since the treatments were being used to save human life.
The Pentagon campaign sought to intensify fears about injecting a pig derivative. As part of an internal investigation at X, the social media company used IP addresses and browser data to identify more than 150 phony accounts that were operated from Tampa by U.S. Central Command and its contractors, according to an internal X document reviewed by Reuters.
“Can you trust China, which tries to hide that its vaccine contains pork gelatin and distributes it in Central Asia and other Muslim countries where many people consider such a drug haram?” read an April 2021 tweet sent from a military-controlled account identified by X.
The Pentagon also covertly spread its messages on Facebook and Instagram, alarming executives at parent company Meta who had long been tracking the military accounts, according to former military officials.
One military-created meme targeting Central Asia showed a pig made out of syringes, according to two people who viewed the image. Reuters found similar posts that traced back to U.S. Central Command. One shows a Chinese flag as a curtain separating Muslim women in hijabs and pigs stuck with vaccine syringes. In the center is a man with syringes; on his back is the word “China.” It targeted Central Asia, including Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, a country that distributed tens of millions of doses of China’s vaccines and participated in human trials. Translated into English, the X post reads: “China distributes a vaccine made of pork gelatin.”
Facebook executives had first approached the Pentagon in the summer of 2020, warning the military that Facebook workers had easily identified the military’s phony accounts, according to three former U.S. officials and another person familiar with the matter. The government, Facebook argued, was violating Facebook’s policies by operating the bogus accounts and by spreading COVID misinformation.
The military argued that many of its fake accounts were being used for counterterrorism and asked Facebook not to take down the content, according to two people familiar with the exchange. The Pentagon pledged to stop spreading COVID-related propaganda, and some of the accounts continued to remain active on Facebook.
Nonetheless, the anti-vax campaign continued into 2021 as Biden took office.
Angered that military officials had ignored their warning, Facebook officials arranged a Zoom meeting with Biden’s new National Security Council shortly after the inauguration, Reuters learned. The discussion quickly became tense.
“It was terrible,” said a senior administration official describing the reaction after learning of the campaign’s pig-related posts. “I was shocked. The administration was pro-vaccine and our concern was this could affect vaccine hesitancy, especially in developing countries.”
By spring 2021, the National Security Council ordered the military to stop all anti-vaccine messaging. “We were told we needed to be pro-vaccine, pro all vaccines,” said a former senior military officer who helped oversee the program. Even so, Reuters found some anti-vax posts that continued through April and other deceptive COVID-related messaging that extended into that summer. Reuters could not determine why the campaign didn’t end immediately with the NSC’s order. In response to questions from Reuters, the NSC declined to comment.
The senior Defense Department official said that those complaints led to an internal review in late 2021, which uncovered the anti-vaccine operation. The probe also turned up other social and political messaging that was “many, many leagues away” from any acceptable military objective. The official would not elaborate.
The review intensified the following year, the official said, after a group of academic researchers at Stanford University flagged some of the same accounts as pro-Western bots in a public report. The high-level Pentagon review was first reported by the Washington Post. which also reported that the military used fake social media accounts to counter China’s message that COVID came from the United States. But the Post report did not reveal that the program evolved into the anti-vax propaganda campaign uncovered by Reuters.
The senior defense official said the Pentagon has rescinded parts of Esper’s 2019 order that allowed military commanders to bypass the approval of U.S. ambassadors when waging psychological operations. The rules now mandate that military commanders work closely with U.S. diplomats in the country where they seek to have an impact. The policy also restricts psychological operations aimed at “broad population messaging,” such as those used to promote vaccine hesitancy during COVID.
The Pentagon’s audit concluded that the military’s primary contractor handling the campaign, General Dynamics IT, had employed sloppy tradecraft, taking inadequate steps to hide the origin of the fake accounts, said a person with direct knowledge of the review. The review also found that military leaders didn’t maintain enough control over its psyop contractors, the person said.
A spokesperson for General Dynamics IT declined to comment.
Nevertheless, the Pentagon’s clandestine propaganda efforts are set to continue. In an unclassified strategy document last year, top Pentagon generals wrote that the U.S. military could undermine adversaries such as China and Russia using “disinformation spread across social media, false narratives disguised as news, and similar subversive activities [to] weaken societal trust by undermining the foundations of government.”
And in February, the contractor that worked on the anti-vax campaign – General Dynamics IT – won a $493 million contract. Its mission: to continue providing clandestine influence services for the military.

EU Council has withdrawn the vote on Chat Control
By Alex Ivanovs Published 20/06/2024
The EU Council and its participants have decided to withdraw the vote on the contentious Chat Control plan proposed by Belgium, the current EU President.
According to Netzpolitik (German), “The EU Council did not make a decision on chat control today, as the agenda item was removed due to the lack of a majority, confirmed by Council and member state spokespersons”.
Belgium’s draft law, which was supposed to be adopted as the Council’s negotiating position, was instead postponed indefinitely. Although the Committee of Permanent Representatives meets weekly, Belgium cannot currently present a proposal that would gain a majority. In July, the Council Presidency will transfer from Belgium to Hungary, which has stated its intention to advance negotiations on chat control as part of its work program.
At the start of 2022, the European Commission proposed monitoring all chat messages and other forms of digital communication among citizens. This initiative includes client-side scanning for end-to-end encrypted services, meaning all messages would be checked irrespective of suspicion.
The plan targets the detection of both known and unknown abusive material and grooming activities. Experts have cautioned that such measures are prone to generating numerous false positives, particularly when identifying unknown content, leading to innocent citizens being misidentified as senders of abusive material.
European legislation is formed through a trialogue process involving negotiations between the European Commission, the European Parliament, and the Council of Ministers. Initially, the European Parliament rejected the European Commission’s proposal and introduced its own, which, while still critical, excluded end-to-end encrypted services. However, Belgium’s new proposal reintroduced client-side scanning for these services, stipulating that users must consent to chat controls; otherwise, they would lose the ability to send photos, videos, and URLs.
This method, termed “upload moderation” by Belgium, has been criticized by opponents as merely a rebranding of the original concept.
Signal and other apps threaten to leave the EU if the proposal is enacted as law
Meredith Whittaker, president of the chat app Signal, has been vocal against these plans. She argues that implementing such measures within end-to-end encrypted communications fundamentally undermines encryption and introduces significant vulnerabilities in the digital infrastructure.
Whittaker emphasizes that these vulnerabilities have far-reaching global implications, not just within Europe. She has repeatedly highlighted the issue, stating, “There is no way to implement such proposals without fundamentally undermining encryption and introducing dangerous vulnerabilities.”
On June 17, Whittaker published an official position condemning the EU’s proposed “upload moderation” as a rebranding of client-side scanning that fundamentally undermines end-to-end encryption.
She emphasized that despite attempts to mask the dangers through marketing, these measures expose encrypted communications to mass surveillance, creating vulnerabilities exploitable by hackers and hostile nations. Whittaker urged a cessation of such rhetorical games, reiterating that any form of mandated mass scanning compromises encryption, thereby threatening global security and privacy at a critically unstable geopolitical moment.
The privacy messenger Threema published a blog post saying the EU’s proposed Chat Control bill represents a dangerous mass surveillance initiative that would undermine data security, violate privacy rights, and negatively impact professionals and minors.
Patrick Breyer, the outgoing MEP from the Pirate Party, raised concerns, noting that proponents of chat control have leveraged the period following the European elections, when attention is lower and the European Parliament is in transition, to advance their agenda. Breyer has called on European citizens to take action and urge their politicians to oppose the measures.
Edward Snowden, the NSA whistleblower, criticized the proposal, stating, “EU apparatchiks are trying to legislate a terrible mass surveillance measure, despite universal public opposition (no sane person wants this), by inventing a new word for it – upload moderation – and hoping no one finds out what it is until it’s too late.”
What happens next?
With the EU Council withdrawing the vote on the Chat Control proposal today, the legislative process faces new uncertainty. The proposal will return to the drawing board, as the European Commission[1] and the European Parliament continue to deliberate on the best way forward.
The discussions will resume after the summer, once the new Parliament is seated and Hungary assumes the Council presidency from Belgium in July. Hungary has already committed to developing a comprehensive legislative framework to prevent and combat online child sexual abuse and revising the directive against the sexual exploitation of children.
The forthcoming negotiations are anticipated to be highly contentious, especially since the European Parliament has firmly opposed any measures that would circumvent end-to-end encryption. The Member States and the Parliament have until April 2026 to agree. This deadline is crucial, as an existing exemption allowing social networks to self-moderate content will expire, potentially eliminating current safeguards against sharing sensitive images.
In the meantime, privacy advocates and digital rights organizations will likely continue to voice their concerns, urging EU citizens to remain vigilant and engaged in the debate over digital privacy and surveillance. The next steps will involve intense negotiations and potential revisions to address the complex issues at stake.
[footnote #1]: On June 20, at the European Data Protection Supervisor (EDPS) 20th anniversary summit, EU Commissioner for Justice Vera Jourová stated that the European Commission’s proposal for the Child Sexual Abuse Regulation (CSAR) would break encryption. This marks the first time the European Commission has publicly acknowledged that the CSAR proposal would compromise encryption, a significant departure from the stance maintained over the past three years by Home Affairs Commissioner Ylva Johansson, who consistently claimed that the proposal would not affect encryption.

Scientists Are Getting Eerily Good at Using WiFi to 'See' People Through Walls in Detail
The signals from WiFi can be used to map a human body, according to a new paper.

January 17, 2023, 7:50pm
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University developed a method for detecting the three dimensional shape and movements of human bodies in a room, using only WiFi routers.
To do this, they used DensePose, a system for mapping all of the pixels on the surface of a human body in a photo. DensePose was developed by London-based researchers and Facebook’s AI researchers. From there, according to their recently-uploaded preprint paper published on arXiv, they developed a deep neural network that maps WiFi signals’ phase and amplitude sent and received by routers to coordinates on human bodies.
Researchers have been working on “seeing” people without using cameras or expensive LiDAR hardware for years. In 2013, a team of researchers at MIT found a way to use cell phone signals to see through walls; in 2018, another MIT team used WiFi to detect people in another room and translate their movements to walking stick-figures.
The Carnegie Mellon researchers wrote that they believe WiFi signals “can serve as a ubiquitous substitute” for normal RGB cameras, when it comes to “sensing” people in a room. Using WiFi, they wrote, overcomes obstacles like poor lighting and occlusion that regular camera lenses face.
Interestingly, they position this advancement as progress in privacy rights; “In addition, they protect individuals’ privacy and the required equipment can be bought at a reasonable price,” they wrote. “In fact, most households in developed countries already have WiFi at home, and this technology may be scaled to monitor the well-being of elder people or just identify suspicious behaviors at home.”
They don’t mention what “suspicious behaviors” might include, if this technology ever hits the mainstream market. But considering companies like Amazon are trying to put Ring camera drones inside our houses, it’s easy to imagine how widespread WiFi-enabled human-detection could be a force for good—or yet another exploitation of all of our privacy.

Why the Internet Isn’t Fun Anymore
The social-media Web as we knew it, a place where we consumed the posts of our fellow-humans and posted in return, appears to be over.
By Kyle Chayka October 9, 2023

Lately on X, the platform formerly known as Twitter, my timeline is filled with vapid posts orbiting the same few topics like water whirlpooling down a drain. Last week, for instance, the chatter was dominated by talk of Taylor Swift’s romance with the football player Travis Kelce. If you tried to talk about anything else, the platform’s algorithmic feed seemed to sweep you into irrelevance. Users who pay for Elon Musk’s blue-check verification system now dominate the platform, often with far-right-wing commentary and outright disinformation; Musk rewards these users monetarily based on the engagement that their posts drive, regardless of their veracity. The decay of the system is apparent in the spread of fake news and mislabelled videos related to Hamas’s attack on Israel.
Elsewhere online, things are similarly bleak. Instagram’s feed pushes months-old posts and product ads instead of photos from friends. Google search is cluttered with junky results, and S.E.O. hackers have ruined the trick of adding “Reddit” to searches to find human-generated answers. Meanwhile, Facebook’s parent company, Meta, in its latest bid for relevance, is reportedly developing artificial-intelligence chatbots with various “sassy” personalities that will be added to its apps, including a role-playing D. & D. Dungeon Master based on Snoop Dogg. The prospect of interacting with such a character sounds about as appealing as texting with one of those spam bots that asks you if they have the right number.
The social-media Web as we knew it, a place where we consumed the posts of our fellow-humans and posted in return, appears to be over. The precipitous decline of X is the bellwether for a new era of the Internet that simply feels less fun than it used to be. Remember having fun online? It meant stumbling onto a Web site you’d never imagined existed, receiving a meme you hadn’t already seen regurgitated a dozen times, and maybe even playing a little video game in your browser. These experiences don’t seem as readily available now as they were a decade ago. In large part, this is because a handful of giant social networks have taken over the open space of the Internet, centralizing and homogenizing our experiences through their own opaque and shifting content-sorting systems. When those platforms decay, as Twitter has under Elon Musk, there is no other comparable platform in the ecosystem to replace them. A few alternative sites, including Bluesky and Discord, have sought to absorb disaffected Twitter users. But like sproutlings on the rain-forest floor, blocked by the canopy, online spaces that offer fresh experiences lack much room to grow.
One Twitter friend told me, of the platform’s current condition, “I’ve actually experienced quite a lot of grief over it.” It may seem strange to feel such wistfulness about a site that users habitually referred to as a “hellsite.” But I’ve heard the same from many others who once considered Twitter, for all its shortcomings, a vital social landscape. Some of them still tweet regularly, but their messages are less likely to surface in my Swift-heavy feed. Musk recently tweeted that the company’s algorithm “tries to optimize time spent on X” by, say, boosting reply chains and downplaying links that might send people away from the platform. The new paradigm benefits tech-industry “thread guys,” prompt posts in the “what’s your favorite Marvel movie” vein, and single-topic commentators like Derek Guy, who tweets endlessly about menswear. Algorithmic recommendations make already popular accounts and subjects even more so, shutting out the smaller, more magpie-ish voices that made the old version of Twitter such a lively destination. (Guy, meanwhile, has received so much algorithmic promotion under Musk that he accumulated more than half a million followers.)
The Internet today feels emptier, like an echoing hallway, even as it is filled with more content than ever. It also feels less casually informative. Twitter in its heyday was a source of real-time information, the first place to catch wind of developments that only later were reported in the press. Blog posts and TV news channels aggregated tweets to demonstrate prevailing cultural trends or debates. Today, they do the same with TikTok posts—see the many local-news reports of dangerous and possibly fake “TikTok trends”—but the TikTok feed actively dampens news and political content, in part because its parent company is beholden to the Chinese government’s censorship policies. Instead, the app pushes us to scroll through another dozen videos of cooking demonstrations or funny animals. In the guise of fostering social community and user-generated creativity, it impedes direct interaction and discovery.
According to Eleanor Stern, a TikTok video essayist with nearly a hundred thousand followers, part of the problem is that social media is more hierarchical than it used to be. “There’s this divide that wasn’t there before, between audiences and creators,” Stern said. The platforms that have the most traction with young users today—YouTube, TikTok, and Twitch—function like broadcast stations, with one creator posting a video for her millions of followers; what the followers have to say to one another doesn’t matter the way it did on the old Facebook or Twitter. Social media “used to be more of a place for conversation and reciprocity,” Stern said. Now conversation isn’t strictly necessary, only watching and listening.
Posting on social media might be a less casual act these days, as well, because we’ve seen the ramifications of blurring the border between physical and digital lives. Instagram ushered in the age of self-commodification online—it was the platform of the selfie—but TikTok and Twitch have turbocharged it. Selfies are no longer enough; video-based platforms showcase your body, your speech and mannerisms, and the room you’re in, perhaps even in real time. Everyone is forced to perform the role of an influencer. The barrier to entry is higher and the pressure to conform stronger. It’s no surprise, in this environment, that fewer people take the risk of posting and more settle into roles as passive consumers.
The patterns of life offscreen affect the makeup of the digital world, too. Having fun online was something that we used to do while idling in office jobs: stuck in front of computers all day, we had to find something on our screens to fill the down time. An earlier generation of blogs such as the Awl and Gawker seemed designed for aimless Internet surfing, delivering intermittent gossip, amusing videos, and personal essays curated by editors with quirky and individuated tastes. (When the Awl closed, in 2017, Jia Tolentino lamented the demise of “online freedom and fun.”) Now, in the aftermath of the pandemic, amid ongoing work-from-home policies, office workers are less tethered to their computers, and perhaps thus less inclined to chase likes on social media. They can walk away from their desks and take care of their children, walk their dog, or put their laundry in. This might have a salutary effect on individuals, but it means that fewer Internet-obsessed people are furiously creating posts for the rest of us to consume. The user growth rate of social platforms over all has slowed over the past several years; according to one estimate, it is down to 2.4 per cent in 2023.
That earlier generation of blogs once performed the task of aggregating news and stories from across the Internet. For a while, it seemed as though social-media feeds could fulfill that same function. Now it’s clear that the tech companies have little interest in directing users to material outside of their feeds. According to Axios, the top news and media sites have seen “organic referrals” from social media drop by more than half over the past three years. As of last week, X no longer displays the headlines for articles that users link to. The decline in referral traffic disrupts media business models, further degrading the quality of original content online. The proliferation of cheap, instant A.I.-generated content promises to make the problem worse.
Choire Sicha, the co-founder of the Awl and now an editor at New York, told me that he traces the seeds of social media’s degradation back a decade. “If I had a time machine I’d go back and assassinate 2014,” he said. That was the year of viral phenomena such as Gamergate, when a digital mob of disaffected video-game fans targeted journalists and game developers on social media; Ellen DeGeneres’s selfie with a gaggle of celebrities at the Oscars, which got retweeted millions of times; and the brief, wondrous fame of Alex, a random teen retail worker from Texas who won attention for his boy-next-door appearance. In those events, we can see some of the nascent forces that would solidify in subsequent years: the tyranny of the loudest voices; the entrenchment of traditional fame on new platforms; the looming emptiness of the content that gets most furiously shared and promoted. But at that point they still seemed like exceptions rather than the rule.
I have been trying to recall the times I’ve had fun online unencumbered by anonymous trolling, automated recommendations, or runaway monetization schemes. It was a long time ago, before social networks became the dominant highways of the Internet. What comes to mind is a Web site called Orisinal that hosted games made with Flash, the late interactive animation software that formed a significant part of the kitschy Internet of the two-thousands, before everyone began posting into the same platform content holes. The games on the site were cartoonish, cute, and pastel-colored, involving activities like controlling a rabbit jumping on stars into the sky or helping mice make a cup of tea. Orisinal was there for anyone to stumble upon, without the distraction of follower counts or sponsored content. You could e-mail the site to a friend, but otherwise there was nothing to share. That old version of the Internet is still there, but it’s been eclipsed by the modes of engagement that the social networks have incentivized. Through Reddit, I recently dug up an emulator of all the Orisinal games and quickly got absorbed into one involving assisting deer leaping across a woodland gap. My only reward was a personal high score. But it was more satisfying, and less lonely, than the experience these days on X. ♦

Underage Workers Are Training AI
Companies that provide Big Tech with AI data-labeling services are inadvertently hiring young teens to work on their platforms, often exposing them to traumatic content.

Like most kids his age, 15-year-old Hassan spent a lot of time online. Before the pandemic, he liked playing football with local kids in his hometown of Burewala in the Punjab region of Pakistan. But Covid lockdowns made him something of a recluse, attached to his mobile phone. “I just got out of my room when I had to eat something,” says Hassan, now 18, who asked to be identified under a pseudonym because he was afraid of legal action. But unlike most teenagers, he wasn’t scrolling TikTok or gaming. From his childhood bedroom, the high schooler was working in the global artificial intelligence supply chain, uploading and labeling data to train algorithms for some of the world’s largest AI companies.
The raw data used to train machine-learning algorithms is first labeled by humans, and human verification is also needed to evaluate their accuracy. This data-labeling ranges from the simple—identifying images of street lamps, say, or comparing similar ecommerce products—to the deeply complex, such as content moderation, where workers classify harmful content within data scraped from all corners of the internet. These tasks are often outsourced to gig workers, via online crowdsourcing platforms such as Toloka, which was where Hassan started his career.
A friend put him on to the site, which promised work anytime, from anywhere. He found that an hour’s labor would earn him around $1 to $2, he says, more than the national minimum wage, which was about $0.26 at the time. His mother is a homemaker, and his dad is a mechanical laborer. “You can say I belong to a poor family,” he says. When the pandemic hit, he needed work more than ever. Confined to his home, online and restless, he did some digging, and found that Toloka was just the tip of the iceberg.
“AI is presented as a magical box that can do everything,” says Saiph Savage, director of Northeastern University’s Civic AI Lab. “People just simply don’t know that there are human workers behind the scenes.”
At least some of those human workers are children. Platforms require that workers be over 18, but Hassan simply entered a relative’s details and used a corresponding payment method to bypass the checks—and he wasn’t alone in doing so. WIRED spoke to three other workers in Pakistan and Kenya who said they had also joined platforms as minors, and found evidence that the practice is widespread.
“When I was still in secondary school, so many teens discussed online jobs and how they joined using their parents' ID,” says one worker who joined Appen at 16 in Kenya, who asked to remain anonymous. After school, he and his friends would log on to complete annotation tasks late into the night, often for eight hours or more.
Appen declined to give an attributable comment.
“If we suspect a user has violated the User Agreement, Toloka will perform an identity check and request a photo ID and a photo of the user holding the ID,” Geo Dzhikaev, head of Toloka operations, says.
Driven by a global rush into AI, the global data labeling and collection industry is expected to grow to over $17.1 billion by 2030, according to Grand View Research, a market research and consulting company. Crowdsourcing platforms such as Toloka, Appen, Clickworker, Teemwork.AI, and OneForma connect millions of remote gig workers in the global south to tech companies located in Silicon Valley. Platforms post micro-tasks from their tech clients, which have included Amazon, Microsoft Azure, Salesforce, Google, Nvidia, Boeing, and Adobe. Many platforms also partner with Microsoft’s own data services platform, the Universal Human Relevance System (UHRS).
These workers are predominantly based in East Africa, Venezuela, Pakistan, India, and the Philippines—though there are even workers in refugee camps, who label, evaluate, and generate data. Workers are paid per task, with remuneration ranging from a cent to a few dollars—although the upper end is considered something of a rare gem, workers say. “The nature of the work often feels like digital servitude—but it's a necessity for earning a livelihood,” says Hassan, who also now works for Clickworker and Appen.
Sometimes, workers are asked to upload audio, images, and videos, which contribute to the data sets used to train AI. Workers typically don’t know exactly how their submissions will be processed, but these can be pretty personal: On Clickworker’s worker jobs tab, one task states: “Show us you baby/child! Help to teach AI by taking 5 photos of your baby/child!” for €2 ($2.15). The next says: “Let your minor (aged 13-17) take part in an interesting selfie project!”
Some tasks involve content moderation—helping AI distinguish between innocent content and that which contains violence, hate speech, or adult imagery. Hassan shared screen recordings of tasks available the day he spoke with WIRED. One UHRS task asked him to identify “fuck,” “c**t,” “dick,” and “bitch” from a body of text. For Toloka, he was shown pages upon pages of partially naked bodies, including sexualized images, lingerie ads, an exposed sculpture, and even a nude body from a Renaissance-style painting. The task? Decipher the adult from the benign, to help the algorithm distinguish between salacious and permissible torsos.
Hassan recalls moderating content while under 18 on UHRS that, he says, continues to weigh on his mental health. He says the content was explicit: accounts of rape incidents, lifted from articles quoting court records; hate speech from social media posts; descriptions of murders from articles; sexualized images of minors; naked images of adult women; adult videos of women and girls from YouTube and TikTok.
Many of the remote workers in Pakistan are underage, Hassan says. He conducted a survey of 96 respondents on a Telegram group chat with almost 10,000 UHRS workers, on behalf of WIRED. About a fifth said they were under 18.
Awais, 20, from Lahore, who spoke on condition that his first name not be published, began working for UHRS via Clickworker at 16, after he promised his girlfriend a birthday trip to the turquoise lakes and snow-capped mountains of Pakistan’s northern region. His parents couldn’t help him with the money, so he turned to data work, joining using a friend’s ID card. “It was easy,” he says.
He worked on the site daily, primarily completing Microsoft’s “Generic Scenario Testing Extension” task. This involved testing homepage and search engine accuracy. In other words, did selecting “car deals” on the MSN homepage bring up photos of cars? Did searching “cat” on Bing show feline images? He was earning $1 to $3 each day, but he found the work both monotonous and infuriating. At times he found himself working 10 hours for $1, because he had to do unpaid training to access certain tasks. Even when he passed the training, there might be no task to complete; or if he breached the time limit, they would suspend his account, he says. Then seemingly out of nowhere, he got banned from performing his most lucrative task—something workers say happens regularly. Bans can occur for a host of reasons, such as giving incorrect answers, answering too fast, or giving answers that deviate from the average pattern of other workers. He’d earned $70 in total. It was almost enough to take his high school sweetheart on the trip, so Awais logged off for good.
Clickworker did not respond to requests for comment. Microsoft declined to comment.
“In some instances, once a user finishes the training, the quota of responses has already been met for that project and the task is no longer available,” Dzhikaev said. “However, should other similar tasks become available, they will be able to participate without further training.”
Researchers say they’ve found evidence of underage workers in the AI industry elsewhere in the world. Julian Posada, assistant professor of American Studies at Yale University, who studies human labor and data production in the AI industry, says that he’s met workers in Venezuela who joined platforms as minors.
Bypassing age checks can be pretty simple. The most lenient platforms, like Clickworker and Toloka, simply ask workers to state they are over 18; the most secure, such as Remotasks, employ face recognition technology to match workers to their photo ID. But even that is fallible, says Posada, citing one worker who says he simply held the phone to his grandmother’s face to pass the checks. The sharing of a single account within family units is another way minors access the work, says Posada. He found that in some Venezuelan homes, when parents cook or run errands, children log on to complete tasks. He says that one family of six he met, with children as young as 13, all claimed to share one account. They ran their home like a factory, Posada says, so that two family members were at the computers working on data labeling at any given point. “Their backs would hurt because they have been sitting for so long. So they would take a break, and then the kids would fill in,” he says.
The physical distances between the workers training AI and the tech giants at the other end of the supply chain—“the deterritorialization of the internet,” Posada calls it—creates a situation where whole workforces are essentially invisible, governed by a different set of rules, or by none.
The lack of worker oversight can even prevent clients from knowing if workers are keeping their income. One Clickworker user in India, who requested anonymity to avoid being banned from the site, told WIRED he “employs” 17 UHRS workers in one office, providing them with a computer, mobile, and internet, in exchange for half their income. While his workers are aged between 18 and 20, due to Clickworker’s lack of age certification requirements, he knows of teenagers using the platform.
In the more shadowy corners of the crowdsourcing industry, the use of child workers is overt.
Captcha (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) solving services, where crowdsourcing platforms pay humans to solve captchas, are a less understood part in the AI ecosystem. Captchas are designed to distinguish a bot from a human—the most notable example being Google’s reCaptcha, which asks users to identify objects in images to enter a website. The exact purpose of services that pay people to solve them remains a mystery to academics, says Posada. “But what I can confirm is that many companies, including Google's reCaptcha, use these services to train AI models,” he says. “Thus, these workers indirectly contribute to AI advancements.”
Google did not respond to a request for comment in time for publication.
There are at least 152 active services, mostly based in China, with more than half a million people working in the underground reCaptcha market, according to a 2019 study by researchers from Zhejiang University in Hangzhou.
“Stable job for everyone. Everywhere,” one service, Kolotibablo, states on its website. The company has a promotional website dedicated to showcasing its worker testimonials, which includes images of young children from across the world. In one, a smiling Indonesian boy shows his 11th birthday cake to the camera. “I am very happy to be able to increase my savings for the future,” writes another, no older than 7 or 8. A 14-year-old girl in a long Hello Kitty dress shares a photo of her workstation: a laptop on a pink, Barbie-themed desk.
Not every worker WIRED interviewed felt frustrated with the platforms. At 17, most of Younis Hamdeen’s friends were waiting tables. But the Pakistani teen opted to join UHRS via Appen instead, using the platform for three or four hours a day, alongside high school, earning up to $100 a month. Comparing products listed on Amazon was the most profitable task he encountered. “I love working for this platform,” Hamdeen, now 18, says, because he is paid in US dollars—which is rare in Pakistan—and so benefits from favorable exchange rates.
But the fact that the pay for this work is incredibly low compared to the wages of in-house employees of the tech companies, and that the benefits of the work flow one way—from the global south to the global north, leads to uncomfortable parallels. “We do have to consider the type of colonialism that is being promoted with this type of work,” says the Civic AI Lab’s Savage.
Hassan recently got accepted to a bachelor’s program in medical lab technology. The apps remain his sole income, working an 8 am to 6 pm shift, followed by 2 am to 6 am. However, his earnings have fallen to just $100 per month, as demand for tasks has outstripped supply, as more workers have joined since the pandemic.
He laments that UHRS tasks can pay as little as 1 cent. Even on higher-paid jobs, such as occasional social media tasks on Appen, the amount of time he needs to spend doing unpaid research means he needs to work five or six hours to complete an hour of real-time work, all to earn $2, he says.
“It’s digital slavery,” says Hassan.
Pop Culture Has Become an Oligopoly
A cartel of superstars has conquered culture. How did it happen, and what should we do about it?
Adam Mastroianni May 02, 2022
You may have noticed that every popular movie these days is a remake, reboot, sequel, spinoff, or cinematic universe expansion. In 2021, only one of the ten top-grossing films––the Ryan Reynolds vehicle Free Guy––was an original. There were only two originals in 2020’s top 10, and none at all in 2019.
People blame this trend on greedy movie studios or dumb moviegoers or competition from Netflix or humanity running out of ideas. Some say it’s a sign of the end of movies. Others claim there’s nothing new about this at all.
Some of these explanations are flat-out wrong; others may contain a nugget of truth. But all of them are incomplete, because this isn’t just happening in movies. In every corner of pop culture––movies, TV, music, books, and video games––a smaller and smaller cartel of superstars is claiming a larger and larger share of the market. What used to be winners-take-some has grown into winners-take-most and is now verging on winners-take-all. The (very silly) word for this oligopoly, like a monopoly but with a few players instead of just one.
I’m inherently skeptical of big claims about historical shifts. I recently published a paper showing that people overestimate how much public opinion has changed over the past 50 years, so naturally I’m on the lookout for similar biases here. But this shift is not an illusion. It’s big, it’s been going on for decades, and it’s happening everywhere you look. So let’s get to the bottom of it.
(Data and code available here.)
Movies
At the top of the box office charts, original films have gone extinct.
I looked at the 20 top-grossing movies going all the way back to 1977 (source), and I coded whether each was part of what film scholars call a “multiplicity”—sequels, prequels, franchises, spin-offs, cinematic universe expansions, etc. This required some judgment calls. Lots of movies are based on books and TV shows, but I only counted them as multiplicities if they were related to a previous movie. So 1990’s Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles doesn’t get coded as a multiplicity, but 1991’s Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles II: The Secret of the Ooze does, and so does the 2014 Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles remake. I also probably missed a few multiplicities, especially in earlier decades, since sometimes it’s not obvious that a movie has some connection to an earlier movie.
Regardless, the shift is gigantic. Until the year 2000, about 25% of top-grossing movies were prequels, sequels, spinoffs, remakes, reboots, or cinematic universe expansions. Since 2010, it’s been over 50% ever year. In recent years, it’s been close to 100%.
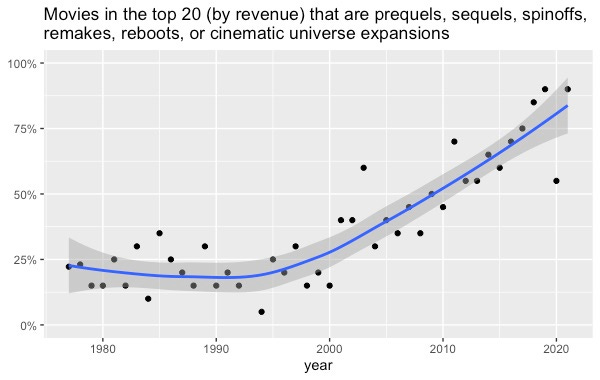
Original movies just aren’t popular anymore, if they even get made in the first place.
Top movies have also recently started taking a larger chunk of the market. I extracted the revenue of the top 20 movies and divided it by the total revenue of the top 200 movies, going all the way back to 1986 (source). The top 20 movies captured about 40% of all revenue until 2015, when they started gobbling up even more.
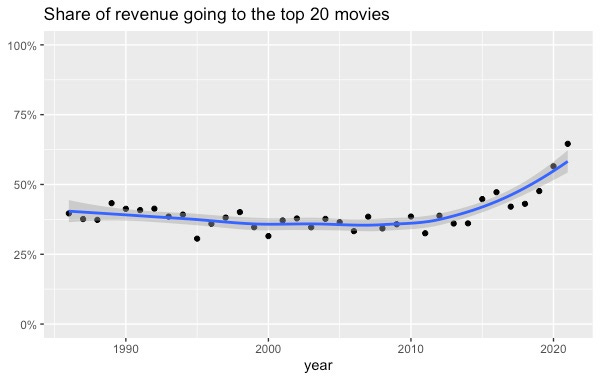
Television
Thanks to cable and streaming, there's way more stuff on TV today than there was 50 years ago. So it would make sense if a few shows ruled the early decades of TV, and now new shows constantly displace each other at the top of the viewership charts.
Instead, the opposite has happened. I pulled the top 30 most-viewed TV shows from 1950 to 2019 (source) and found that fewer and fewer franchises rule a larger and larger share of the airwaves. In fact, since 2000, about a third of the top 30 most-viewed shows are either spinoffs of other shows in the top 30 (e.g., CSI and CSI: Miami) or multiple broadcasts of the same show (e.g., American Idol on Monday and American Idol on Wednesday).

Two caveats to this data. First, I’m probably slightly undercounting multiplicities from earlier decades, where the connections between shows might be harder for a modern viewer like me to understand––maybe one guy hosted multiple different shows, for example. And second, the Nielsen ratings I’m using only recently started accurately measuring viewership on streaming platforms. But even in 2019, only 14% of viewing time was spent on streaming, so this data isn’t missing much.
Music
It used to be that a few hitmakers ruled the charts––The Beatles, The Eagles, Michael Jackson––while today it’s a free-for-all, right?
Nope. A data scientist named Azhad Syed has done the analysis, and he finds that the number of artists on the Billboard Hot 100 has been decreasing for decades.
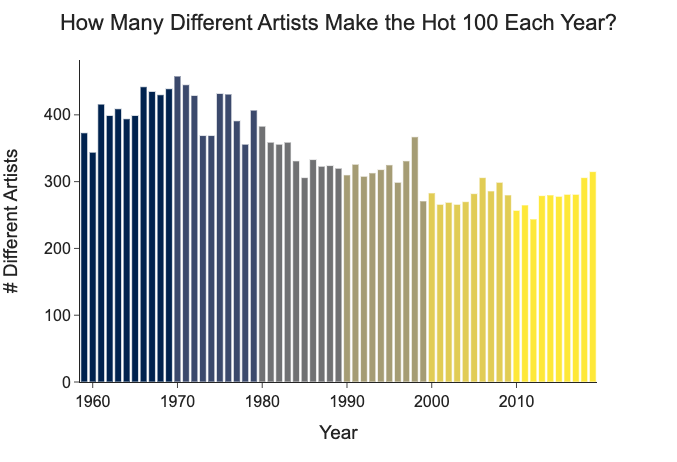
Chart by Azhad Syed
And since 2000, the number of hits per artist on the Hot 100 has been increasing.
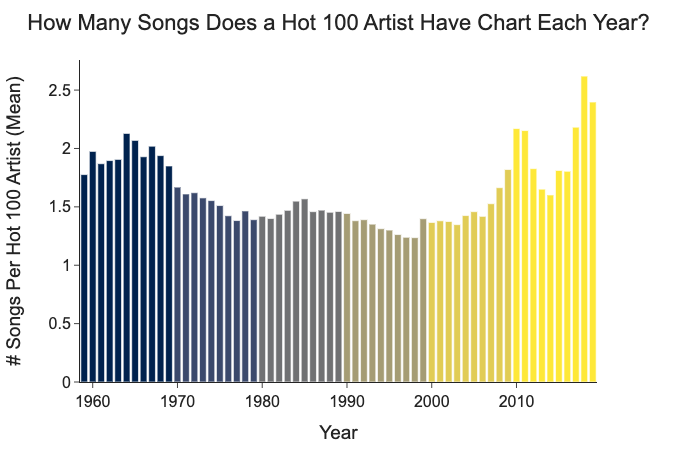
Chart by Azhad Syed
(Azhad says he’s looking for a job––you should hire him!)
A smaller group of artists tops the charts, and they produce more of the chart-toppers. Music, too, has become an oligopoly.
Books
Literature feels like a different world than movies, TV, and music, and yet the trend is the same.
Using LiteraryHub's list of the top 10 bestselling books for every year from 1919 to 2017, I found that the oligopoly has come to book publishing as well. There are a couple ways we can look at this. First, we can look at the percentage of repeat authors in the top 10––that is, the number of books in the top 10 that were written by an author with another book in the top 10.
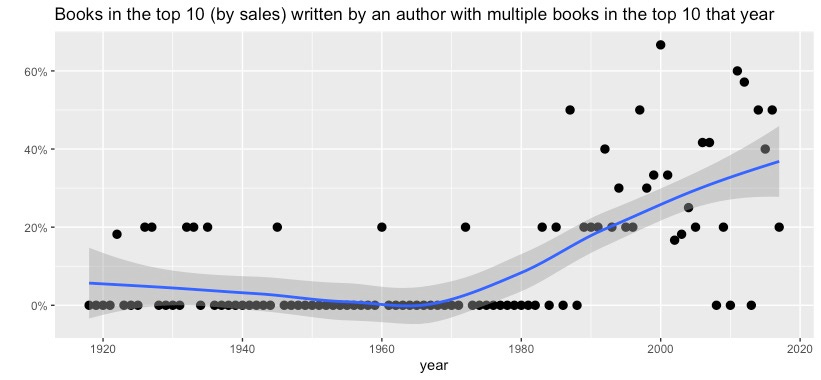
It used to be pretty rare for one author to have multiple books in the top 10 in the same year. Since 1990, it’s happened almost every year. No author ever had three top 10 books in one year until Danielle Steel did it 1998. In 2011, John Grisham, Kathryn Stockett, and Stieg Larsson all had two chart-topping books each.
We can also look at the percentage of authors in the top 10 were already famous––say, they had a top 10 book within the past 10 years. That has increased over time, too.
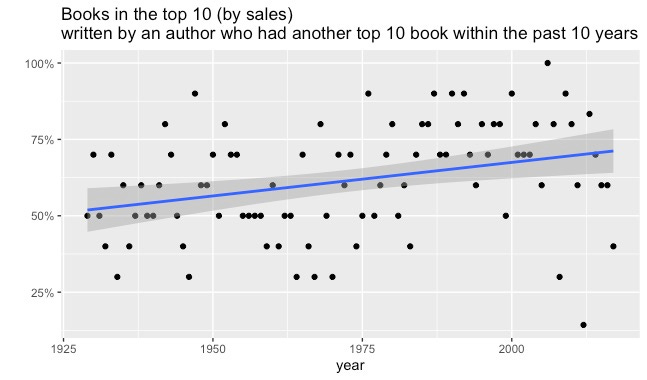
In the 1950s, a little over half of the authors in the top 10 had been there before. These days, it’s closer to 75%.
Video games
I tracked down the top 20 bestselling video games for each year from 1995 to 2021 (sources: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and coded whether each belongs to a preexisting video game franchise. (Some games, like Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone, belong to franchises outside of video games. For these, I coded the first installment as originals and any subsequent installments as franchise games.)
The oligopoly rules video games too:
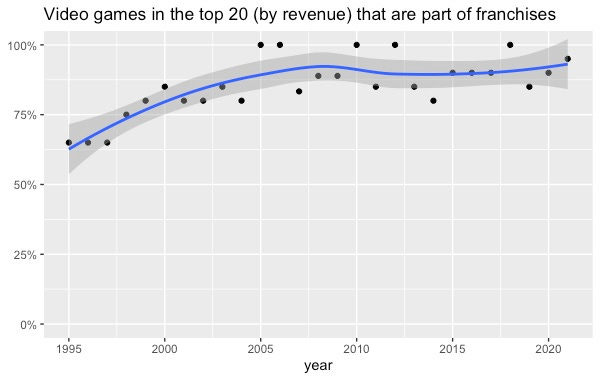
In the late 1990s, 75% or less of bestselling video games were franchise installments. Since 2005, it’s been above 75% every year, and sometimes it’s 100%. At the top of the charts, it’s all Mario, Zelda, Call of Duty, and Grand Theft Auto.
Why is this happening?
Any explanation for the rise of the pop oligopoly has to answer two questions: why have producers started producing more of the same thing, and why are consumers consuming it? I think the answers to the first question are invasion, consolidation, and innovation. I think the answer to the second question is proliferation.
Invasion
Software and the internet have made it easier than ever to create and publish content. Most of the stuff that random amateurs make is crap and nobody looks at it, but a tiny proportion gets really successful. This might make media giants choose to produce and promote stuff that independent weirdos never could, like an Avengers movie. This can’t explain why oligopolization started decades ago––YouTube only launched in 2005, for example, and most Americans didn’t have broadband until 2007––but it might explain why it’s accelerated and stuck around.
Consolidation
Big things like to eat, defeat, and outcompete smaller things. So over time, big things should get bigger and small things should die off. Indeed, movie studios, music labels, TV stations, and publishers of books and video games have all consolidated. Maybe it’s inevitable that major producers of culture will suck up or destroy everybody else, leaving nothing but superstars and blockbusters. Indeed, maybe cultural oligopoly is merely a transition state before we reach cultural monopoly.
Innovation
You may think there’s nothing left to discover in art forms as old as literature and music, and that they simply iterate as fashions change. But it took humans [thousands of years](http://www.essentialvermeer.com/technique/perspective/history.html#:~:text=In its mathematical form%2C linear,De pictura [On Painting]) to figure out how to create the illusion of depth in paintings. Novelists used to think that sentences had to be long and complicated until Hemingway came along, wrote some snappy prose, and changed everything. Even very old art forms, then, may have secrets left to discover. Maybe the biggest players in culture discovered some innovations that won them a permanent, first-mover chunk of market share. I can think of a few:
- In books: lightning-quick plots and chapter-ending cliffhangers. Nobody thinks The Da Vinci Code is high literature, but it’s a book that really really wants you to read it. And a lot of people did!
- In music: sampling. Musicians [seem to sample more often these days](https://www.hypebot.com/hypebot/2019/03/2019-the-state-of-sampling-draft.html#:~:text=1 in 5 Songs on,usually between 20-25%). Now we not only remake songs; we franchise them too.
- In movies, TV, and video games: cinematic universes. Studios have finally figured out that once audiences fall in love with fictional worlds, they want to spend lots of time in them. Marvel, DC, and Star Wars are the most famous, but there are also smaller universe expansions like Better Call Saul and El Camino from Breaking Bad and The Many Saints of Newark from The Sopranos. Video game developers have understood this for even longer, which is why Mario does everything from playing tennis to driving go-karts to, you know, being a piece of paper.
Proliferation
Invasion, consolidation, and innovation can, I think, explain the pop oligopoly from the supply side. But all three require a willing audience. So why might people be more open to experiencing the same thing over and over again?
As options multiply, choosing gets harder. You can’t possibly evaluate everything, so you start relying on cues like “this movie has Tom Hanks in it” or “I liked Red Dead Redemption, so I’ll probably like Red Dead Redemption II,” which makes you less and less likely to pick something unfamiliar.
Another way to think about it: more opportunities means higher opportunity costs, which could lead to lower risk tolerance. When the only way to watch a movie is to go pick one of the seven playing at your local AMC, you might take a chance on something new. But when you’ve got a million movies to pick from, picking a safe, familiar option seems more sensible than gambling on an original.
This could be happening across all of culture at once. Movies don’t just compete with other movies. They compete with every other way of spending your time, and those ways are both infinite and increasing. There are now [60,000](https://www.gutenberg.org/#:~:text=Project Gutenberg is a library of over 60%2C000 free eBooks) free books on Project Gutenberg, Spotify [says](https://newsroom.spotify.com/company-info/#:~:text=Discover%2C manage and share over,ad-free music listening experience) it has 78 million songs and 4 million podcast episodes, and humanity uploads 500 hours of video to YouTube [every minute](https://www.statista.com/statistics/259477/hours-of-video-uploaded-to-youtube-every-minute/#:~:text=As of February 2020%2C more,for online video has grown). So uh, yeah, the Tom Hanks movie sounds good.
What do we do about it?
Some may think that the rise of the pop oligopoly means the decline of quality. But the oligopoly can still make art: Red Dead Redemption II is a terrific game, “Blinding Lights” is a great song, and Toy Story 4 is a pretty good movie. And when you look back at popular stuff from a generation ago, there was plenty of dreck. We’ve forgotten the pulpy Westerns and insipid romances that made the bestseller lists while books like The Great Gatsby, Brave New World, and Animal Farm did not. American Idol is not so different from the televised talent shows of the 1950s. Popular culture has always been a mix of the brilliant and the banal, and nothing I’ve shown you suggests that the ratio has changed.
The problem isn’t that the mean has decreased. It’s that the variance has shrunk. Movies, TV, music, books, and video games should expand our consciousness, jumpstart our imaginations, and introduce us to new worlds and stories and feelings. They should alienate us sometimes, or make us mad, or make us think. But they can’t do any of that if they only feed us sequels and spinoffs. It’s like eating macaroni and cheese every single night forever: it may be comfortable, but eventually you’re going to get scurvy.
We haven’t fully reckoned with what the cultural oligopoly might be doing to us. How much does it stunt our imaginations to play the same video games we were playing 30 years ago? What message does it send that one of the most popular songs in the 2010s was about how a 1970s rock star was really cool? How much does it dull our ambitions to watch 2021’s The Matrix: Resurrections, where the most interesting scene is just Neo watching the original Matrix from 1999? How inspiring is it to watch tiny variations on the same police procedurals and reality shows year after year? My parents grew up with the first Star Wars movie, which had the audacity to create an entire universe. My niece and nephews are growing up with the ninth Star Wars movie, which aspires to move merchandise. Subsisting entirely on cultural comfort food cannot make us thoughtful, creative, or courageous.
Fortunately, there’s a cure for our cultural anemia. While the top of the charts has been oligopolized, the bottom remains a vibrant anarchy. There are weird books and funky movies and bangers from across the sea. Two of the most interesting video games of the past decade put you in the role of an immigration officer and an insurance claims adjuster. Every strange thing, wonderful and terrible, is available to you, but they’ll die out if you don’t nourish them with your attention. Finding them takes some foraging and digging, and then you’ll have to stomach some very odd, unfamiliar flavors. That’s good. Learning to like unfamiliar things is one of the noblest human pursuits; it builds our empathy for unfamiliar people. And it kindles that delicate, precious fire inside us––without it, we might as well be algorithms. Humankind does not live on bread alone, nor can our spirits long survive on a diet of reruns.

Réseaux sociaux : la fabrique de l’hostilité politique ?
Publié: 17 juin 2024, 15:21 CEST
Depuis quelques années, les réseaux sociaux comme Facebook et X (anciennement Twitter) sont devenus la cible d’accusations nombreuses : facteurs de diffusion de « fake news » à grande échelle, instruments de déstabilisation des démocraties par la Russie et la Chine, machines à capturer notre attention pour la vendre à des marchands de toutes sortes, théâtres d’un ciblage publicitaire toujours plus personnalisé et manipulateur, etc. En atteste le succès de documentaires et d’essais sur le coût humain, jugé considérable, des réseaux sociaux, comme The Social Dilemma sur Netflix.
L’un de ces discours, en particulier, rend les plates-formes digitales et leurs algorithmes responsables de l’amplification de l’hostilité en ligne et de la polarisation politique dans la société. Avec les discussions en ligne anonymes, affirment certains, n’importe qui serait susceptible de devenir un troll, c’est-à-dire une personne agressive, cynique et dépourvue de compassion, ou de se « radicaliser ».
Des travaux récents en sciences sociales quantitatives et en psychologie scientifique permettent toutefois d’apporter quelques correctifs à ce récit, excessivement pessimiste.
L’importance du contexte sociopolitique et de la psychologie
Pour commencer, plusieurs études suggèrent que si les individus font régulièrement l’expérience de discussions sur des sujets politiques qui deviennent conflictuelles, cette incivilité est en partie liée à des facteurs psychologiques et socio-économiques qui préexistent aux plates-formes digitales.
Dans une étude interculturelle de grande envergure, nous avons interrogé plus de 15 000 personnes via des panels représentatifs dans trente nations très diverses (France, Irak, Thaïlande, Pakistan, etc.) sur leurs expériences des conversations sur Internet. Notre première découverte est que ce sont dans les pays les plus inégalitaires économiquement et les moins démocratiques que les individus sont le plus souvent l’objet d’invectives hostiles de la part de leurs concitoyens sur les réseaux (comme en Turquie ou au Brésil). Ce phénomène découle manifestement des frustrations générées par ces sociétés plus répressives des aspirations individuelles.
Notre étude montre en outre que les individus qui s’adonnent le plus à l’hostilité en ligne sont aussi ceux qui sont les plus disposés à la recherche de statut social par la prise de risque. Ce trait de personnalité correspond à une orientation vers la dominance, c’est-à-dire à chercher à soumettre les autres à sa volonté (y compris par l’intimidation). Dans nos données interculturelles, nous observons que les individus ayant ce type de traits dominants sont nombreux dans les pays inégalitaires et non démocratiques. Des analyses indépendantes montrent d’ailleurs que la dominance est un élément clé de la psychologie de la conflictualité politique, puisqu’elle prédit également davantage de partage de ‘fake news’ moquant ou insultant les opposants politiques sur Internet, et plus d’attrait pour le conflit politique hors ligne, notamment.
Répliquant une étude antérieure, nous trouvons par ailleurs que ces individus motivés par la recherche de statut par la prise de risque, qui admettent le plus se comporter de manière hostile sur Internet, sont aussi ceux qui sont plus susceptibles d’interagir de manière agressive ou toxique dans des discussions en face à face (la corrélation entre l’hostilité en ligne et hors ligne est forte, de l’ordre de β = 0,77).
En résumé, l’hostilité politique en ligne semble largement être le fruit de personnalités particulières, rendues agressives par les frustrations engendrées par des contextes sociaux inégalitaires, et activant notre tendance à voir le monde en termes de “nous” vs « eux ». Au plan politique, réduire les disparités de richesses entre groupes et rendre nos institutions plus démocratiques constituent des objectifs probablement incontournables si nous souhaitons faire advenir un Internet (et une société civile) plus harmonieux.
Les réseaux : prismes exagérant l’hostilité ambiante
Si notre étude replace l’hostilité politique en ligne dans un plus large contexte, elle ne nie pas tout rôle aux plates-formes dans la production de la polarisation politique pour autant.
Les réseaux sociaux permettent à un contenu d’être diffusé à l’identique à des millions de personnes (à l’inverse de la communication verbale, lieu de distorsions inévitables). À ce titre, ils peuvent mésinformer ou mettre en colère des millions de personnes à un très faible coût. Ceci est vrai que l’information fausse ou toxique soit créée intentionnellement pour générer des clics, ou qu’elle soit le fruit involontaire des biais politiques d’un groupe politique donné.
[Déjà plus de 120 000 abonnements aux newsletters The Conversation. Et vous ? Abonnez-vous aujourd’hui pour mieux comprendre les grands enjeux du monde.]
Si les échanges sur les réseaux sociaux manquent souvent de civilité, c’est également à cause de la possibilité qu’ils offrent d’échanger avec des étrangers anonymes, dépersonnalisés. Cette expérience unique à l’ère Internet réduit le sentiment de responsabilité personnelle, ainsi que l’empathie vis-à-vis d’interlocuteurs que nous ne voyons plus comme des personnes mais comme les membres interchangeables de « tribus » politiques.
Des analyses récentes rappellent par ailleurs que les réseaux sociaux – comme le journalisme, à bien des égards – opèrent moins comme le miroir que comme le prisme déformant de la diversité des opinions dans la société.
Les posts politiques indignés et potentiellement insultants sont souvent le fait de personnes plus déterminées à s’exprimer et radicales que la moyenne – que ce soit pour signaler leurs engagements, exprimer une colère, faire du prosélytisme, etc. Même lorsqu’ils représentent une assez faible proportion de la production écrite sur les réseaux, ces posts se trouvent promus par des algorithmes programmés pour mettre en avant les contenus capables d’attirer l’attention et de déclencher des réponses, dont les messages clivants font partie.
À contrario, la majorité des utilisateurs, plus modérée et moins péremptoire, est réticente à se lancer dans des discussions politiques qui récompensent rarement la bonne foi argumentative et qui dégénèrent souvent en « shitstorms » (c.-à-d., en déchaînements de haine).
Ces biais de sélection et de perception produisent l’impression trompeuse que les convictions radicales et hostiles sont à la fois plus répandues et tolérées moralement qu’elles ne le sont en réalité.
Quand l’exposition à la différence énerve
Ceci étant dit, l’usage des réseaux sociaux semble pouvoir contribuer à augmenter l’hostilité et la radicalité politiques selon un mécanisme au moins : celui de l’exposition à des versions caricaturales et agressives des positions politiques adverses, qui agacent.
Contrairement à une croyance répandue, la plupart de nos connexions virtuelles ne prennent typiquement pas vraiment la forme de « chambres d’écho », nous isolant dans des sas d’idées politiques totalement homogènes.
Bien que certains réseaux soient effectivement construits de cette manière (4Chan ou certains sub-Reddits), les plus larges plates-formes que sont Facebook (3 milliards d’utilisateurs) et X (550 millions) nous font typiquement défiler une certaine diversité d’opinions devant les yeux. Celle-ci est en tous cas fréquemment supérieure à celle de nos relations amicales : êtes-vous encore régulièrement en contact avec des copains de collège qui ont « viré Front national » ? Probablement pas, mais il est plus probable que vous lisiez leurs posts Facebook.
Cette exposition à l’altérité idéologique est désirable, en théorie, puisqu’elle devrait permettre de nous faire découvrir les angles morts de nos connaissances et convictions politiques, notre commune humanité, et donc nous rendre à la fois plus humbles et plus respectueux les uns des autres. Malheureusement, le mode sur lequel la plupart des gens expriment leurs convictions politiques – sur les réseaux comme à la machine à café – est assez dépourvu de nuance et de pédagogie. Il tend à réduire les positions adverses à des caricatures diabolisées, et cherche moins à persuader le camp d’en face qu’à galvaniser les personnes qui sont déjà d’accord avec soi, ou à se faire bien voir d’amis politiques.
Prenant appui sur des études expérimentales déployées sur Twitter et des interviews de militants démocrates et républicains menées avec son équipe, le sociologue Chris Bail nous avertit dans son livre Le prisme des réseaux sociaux. D’après lui, une exposition répétée à des contenus peu convaincants et moqueurs produits par nos ennemis politiques peut paradoxalement renforcer les partisans dans leurs positions et identités préexistantes, plutôt que de les rapprocher intellectuellement et émotionnellement les uns des autres.
Cependant, cette relation entre usage des réseaux sociaux et polarisation politique pourrait dépendre beaucoup du temps d’exposition et n’apparaît pas dans tous les échantillons étudiés. Ainsi, des études explorant les effets d’un arrêt de l’utilisation de Facebook et d’Instagram n’observent pas que l’utilisation de ces médias sociaux polarise de façon détectable les opinions politiques des utilisateurs.
Rappelons-nous toujours que les discours pointant des menaces pesant sur la société jouissent d’un avantage concurrentiel considérable sur le marché des idées et des conversations, en raison de leur attractivité pour nos esprits. Il convient donc d’approcher la question des liens entre réseaux sociaux, hostilité et polarisation politique avec nuance, en évitant les travers symétriques de l’optimisme béat et de la panique collective.

How a Samsung Washing Machine Chime Triggered a YouTube Copyright Fiasco
When YouTube’s Content ID system goes wrong, it goes very, very wrong.
Ashley Belanger, Ars Technica Culture News Jun 1, 2024 11:30 AM
YouTube’s Content ID system—which automatically detects content registered by rights holders—is “completely fucking broken,” a YouTuber called “Albino” declared in a rant on the social media site X that has been viewed more than 950,000 times.
Albino, who is also a popular Twitch streamer, complained that his YouTube video playing through Fallout was demonetized because a Samsung washing machine randomly chimed to signal a laundry cycle had finished while he was streaming.
Apparently, YouTube had automatically scanned Albino's video and detected the washing machine chime as a song called “Done”—which Albino quickly saw was uploaded to YouTube by a musician known as Audego nine years ago.
But when Albino hit Play on Audego's song, the only thing that he heard was a 30-second clip of the washing machine chime. To Albino it was obvious that Audego didn't have any rights to the jingle, which Dexerto reported actually comes from the song "Die Forelle" (“The Trout”) from Austrian composer Franz Schubert.
The song was composed in 1817 and is in the public domain. Samsung has used it to signal the end of a wash cycle for years, sparking debate over whether it's the catchiest washing machine song and inspiring at least one violinist to perform a duet with her machine. It's been a source of delight for many Samsung customers, but for Albino, hearing the jingle appropriated on YouTube only inspired ire.
"A guy recorded his fucking washing machine and uploaded it to YouTube with Content ID," Albino said in a video on X. "And now I'm getting copyright claims" while "my money" is "going into the toilet and being given to this fucking slime."
Albino suggested that YouTube had potentially allowed Audego to make invalid copyright claims for years without detecting the seemingly obvious abuse.
"How is this still here?" Albino asked. "It took me one Google search to figure this out," and "now I'm sharing revenue with this? That's insane."
At first, Team YouTube gave Albino a boilerplate response on X, writing, "We understand how important it is for you. From your vid, it looks like you've recently submitted a dispute. When you dispute a Content ID claim, the person who claimed your video (the claimant) is notified and they have 30 days to respond."
Albino expressed deep frustration at YouTube's response, given how "egregious" he considered the copyright abuse to be.
"Just wait for the person blatantly stealing copyrighted material to respond," Albino responded to YouTube. "Ah, OK, yes, I'm sure they did this in good faith and will make the correct call, though it would be a shame if they simply clicked ‘reject dispute,’ took all the ad revenue money and forced me to risk having my channel terminated to appeal it!! XDxXDdxD!! Thanks Team YouTube!"
Soon after, YouTube confirmed on X that Audego's copyright claim was indeed invalid. The social platform ultimately released the claim and told Albino to expect the changes to be reflected on his channel within two business days.
Ars could not immediately reach YouTube or Albino for comment.
Widespread Abuse of Content ID Continues
YouTubers have complained about abuse of Content ID for years. Techdirt's Timothy Geigner agreed with Albino's assessment that the YouTube system is "hopelessly broken," noting that sometimes content is flagged by mistake. But just as easily, bad actors can abuse the system to claim "content that simply isn’t theirs" and seize sometimes as much as millions in ad revenue.
In 2021, YouTube announced that it had invested "hundreds of millions of dollars" to create content management tools, of which Content ID quickly emerged as the platform's go-to solution to detect and remove copyrighted materials.
At that time, YouTube claimed that Content ID was created as a "solution for those with the most complex rights management needs," like movie studios and record labels whose movie clips and songs are most commonly uploaded by YouTube users. YouTube warned that without Content ID, "rights holders could have their rights impaired and lawful expression could be inappropriately impacted."
Since its rollout, more than 99 percent of copyright actions on YouTube have consistently been triggered automatically through Content ID.
And just as consistently, YouTube has seen widespread abuse of Content ID, terminating "tens of thousands of accounts each year that attempt to abuse our copyright tools," YouTube said. YouTube also acknowledged in 2021 that "just one invalid reference file in Content ID can impact thousands of videos and users, stripping them of monetization or blocking them altogether."
To help rights holders and creators track how much copyrighted content is removed from the platform, YouTube started releasing biannual transparency reports in 2021. The Electronic Frontier Foundation, a nonprofit digital rights group, applauded YouTube's "move towards transparency" while criticizing YouTube's "claim that YouTube is adequately protecting its creators."
"That rings hollow," the EFF reported in 2021, noting that "huge conglomerates have consistently pushed for more and more restrictions on the use of copyrighted material, at the expense of fair use and, as a result, free expression." As the EFF saw it then, YouTube's Content ID system mainly served to appease record labels and movie studios, while creators felt "pressured" not to dispute Content ID claims out of "fear" that their channel might be removed if YouTube consistently sided with rights holders.
According to YouTube, "it’s impossible for matching technology to take into account complex legal considerations like fair use or fair dealing," and that impossibility seemingly ensures that creators bear the brunt of automated actions even when it's fair to use copyrighted materials.
At that time, YouTube described Content ID as "an entirely new revenue stream from ad-supported, user generated content" for rights holders, who made more than $5.5 billion from Content ID matches by December 2020. More recently, YouTube reported that figure climbed above $9 billion, as of December 2022. With so much money at play, it's easy to see how the system could be seen as disproportionately favoring rights holders, while creators continue to suffer from income diverted by the automated system.
Despite YouTubers' ongoing frustrations, not much has changed with YouTube's Content ID system over the years. The language used in YouTube's most recent transparency report is largely a direct copy of the original report from 2021.
And while YouTube claims that the Content ID match technology should be "continually" adapted to sustain a "balanced ecosystem," the few most recent updates YouTube announced in 2022 didn't seem to do much to help creators dispute invalid claims.
"We’ve heard the Content ID Dispute process is top of mind for many of you," YouTube wrote in 2022. "You've shared that the process can take too long and can have long-term impact on your channel, specifically when claims result in viewing restrictions or monetization impact."
To address this, YouTube did not expedite the dispute process, which still allows up to 30 days for rights holders to respond. Instead, it expedited the appeals process, which happens after a rights holder rejects a disputed claim and arguably is the moment when the YouTuber's account is most in danger of being terminated.
"Now, the claimant will have 7 days instead of 30 to review the appeal before deciding whether to request a takedown of the video, release the claim, or let it expire," YouTube wrote in 2022. "We hope shortening the timespan of the appeals process helps you get claims resolved much faster!"
This update would only help YouTubers intent on disputing claims, like Albino was, but not the majority of YouTubers, whom the EFF reported were seemingly so intimidated by disputing Content ID claims that they more commonly just accepted "whatever punishment the system has levied against them." The EFF summarized the predicament that many YouTubers remain stuck in today:
There is a terrible, circular logic that traps creators on YouTube. They cannot afford to dispute Content ID matches because that could lead to DMCA notices. They cannot afford DMCA notices because those lead to copyright strikes. They cannot afford copyright strikes because that could lead to a loss of their account. They cannot afford to lose their account because they cannot afford to lose access to YouTube’s giant audience. And they cannot afford to lose access to that audience because they cannot count on making money from YouTube’s ads alone, partially because Content ID often diverts advertising money to rights holders when there is Content ID match. Which they cannot afford to dispute.
For Albino, who said he has fought back against many Content ID claims, the Samsung washing machine chime triggering demonetization seemed to be the final straw, breaking his patience with YouTube's dispute process.
"It's completely out of hand," Albino wrote on X.
Katharine Trendacosta, a YouTube researcher and the EFF's director of policy and advocacy, agreed with Albino, telling Ars that YouTube's Content ID system has not gotten any better over the years: “It's worse, and it's intentionally opaque and made to be incredibly difficult to navigate" for creators.
"I don't know any YouTube creator who's happy with the way Content ID works," Trendacosta told Ars.
But while many people think that YouTube's system isn't great, Trendacosta also said that she "can't think of a way to build the match technology" to improve it, because "machines cannot tell context." Perhaps if YouTube's matching technology triggered a human review each time, "that might be tenable," but "they would have to hire so many more people to do it."
What YouTube could be doing is updating its policies to make the dispute process less intimidating to content creators, though, Trendacosta told Ars. Right now, the bigger problem for creators, Trendacosta said her research has shown, is not how long it takes for YouTube to work out the dispute process but "the way YouTube phrases the dispute process to discourage you from disputing."
"The system is so discouraging," Trendacosta told Ars, with YouTube warning YouTubers that initiating a dispute could result in a copyright strike that terminates their accounts. "What it ends up doing is making them go, 'You know what, I'll eat it, whatever.'"
YouTube, which has previously dismissed complaints about the Content ID tool by saying "no system is perfect," did not respond to Ars' request for comment on whether any updates to the tool might be coming that might benefit creators. Instead, YouTube's plan seems to be to commiserate with users who likely can't afford to leave the platform over their concerns.
"Totally understand your frustration," Team YouTube told Albino on X.
This story originally appeared on Ars Technica.

Deluge of ‘pink slime’ websites threaten to drown out truth with fake news in US election
US sites pushing misinformation are proliferating, aiming to look like reliable sources as local newspapers close down
Eric Berger Thu 20 Jun 2024 12.00 CEST
Political groups on the right and left are using fake news websites designed to look like reliable sources of information to fill the void left by the demise of local newspapers, raising fears of the impact that they might have during the United States’ bitterly fought 2024 election.
Some media experts are concerned that the so-called pink slime websites, often funded domestically, could prove at least as harmful to political discourse and voters’ faith in media and democracy as foreign disinformation efforts in the 2016 and 2020 presidential elections.
According to a recent report from NewsGuard, a company that aims to counter misinformation by studying and rating news websites, the websites are so prolific that “the odds are now better than 50-50 that if you see a news website purporting to cover local news, it’s fake.”
NewsGuard estimates that there are a staggering 1,265 such fake local news websites in the US – 4% more than the websites of 1,213 daily newspapers left operating in the country.
“Actors on both sides of the political spectrum” feel “that what they are doing isn’t bad because all media is really biased against their side or that that they know actors on the other side are using these tactics and so they feel they need to,” said Matt Skibinski, general manager of NewsGuard, which determined that such sites now outnumber legitimate local news organizations. “It’s definitely contributed to partisanship and the erosion of trust in media; it’s also a symptom of those things.”
Pink slime websites, named after a meat byproduct, started at least as early as 2004 when Brian Timpone, a former television reporter who described himself as a “biased guy” and a Republican, started funding websites featuring names of cities, towns and regions like the Philly Leader and the South Alabama Times.
Timpone’s company, Metric Media, now operates more than 1,000 such websites and his private equity company receives funding from conservative political action committees, according to NewsGuard.
The Leader recently ran a story with the headline, “Rep Evans votes to count illegal aliens towards seats in Congress.”
In actuality, Representative Dwight Evans, a Democrat, did not vote to start counting undocumented immigrants in the 2030 census but rather against legislation that would have changed the way the country has conducted apportionment since 1790.
That sort of story is “standard practice for these outlets”, according to Tim Franklin, who leads Northwestern University’s Local News Initiative, which researches the industry.
“They will take something that maybe has just a morsel of truth to it and then twist it with their own partisan or ideological spin,” Franklin said. “They also tend to do it on issues like immigration or hot-button topics that they think will elicit an emotional response.”
A story published this month on the NW Arkansas News site had a headline on the front page that reported that the unemployment rate in 2021 in Madison county was 5.1% – even though there is much more recent data available. In April 2024, the local unemployment rate was 2.5%.
“Another tactic that we have seen across many of this category of sites is taking a news story that happened at some point and presenting it as if it just happened now, in a way that is misleading,” Skibinski said.
The left has also created websites designed to look like legitimate news organizations but actually shaped by Democratic supporters.
The liberal Courier Newsroom network operates websites in Arizona, Florida, Iowa, Michigan and Nevada, among other states, that – like the conservative pink slime sites – have innocuous sounding names like the Copper Courier and Up North News. The Courier has runs stories like “Gov Ducey Is Now the Most Unpopular Governor in America,” referring to Doug Ducy, the former Republican Arizona governor.
“In contrast, coverage of Democrats, including US President Joe Biden, Democratic Arizona Gov Katie Hobbs, and US Sen Mark Kelly of Arizona, is nearly always laudatory,” NewsGuard stated in a report about Courier coverage.
Tara McGowan, a Democratic strategist who founded the Courier Newsroom has received funding from liberal donors like Reid Hoffman and George Soros, as well as groups associated with political action committees, according to NewsGuard.
“There are pink slime operations on both the right and the left. To me, the key is disclosure and transparency about ownership,” said Franklin.
In a statement, a spokesperson for the Courier said comparisons between its operations and rightwing pink slime groups were unfair and criticized NewsGuard’s methodology in comparing the two.
“Courier publishes award-winning, factual local news by talented journalists who live in the communities we cover, and our reporting is often cited by legacy media outlets. This is in stark contrast to the pink slime networks that pretend to have a local presence but crank out low-quality fake news with no bylines and no accountability. Courier is proudly transparent about our pro-democracy values, and we carry on the respected American tradition of advocacy journalism,” the spokesperson said.
While both the left and the right have invested in the pink slime websites, there are differences in the owners’ approaches, according to Skibinski.
The right-wing networks have created more sites “that are probably getting less attention per site, and on the left, there is a smaller number of sites, but they are more strategic about getting attention to those sites on Facebook and elsewhere”, Skibinski said. “I don’t know that we can quantify whether one is more impactful than the other.”
Artificial intelligence could also help site operators quickly generate stories and create fake images.
“The technology underlying artificial intelligence is now becoming more accessible to malign actors,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, a University of Pennsylvania communications professor and director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center, which publishes Factcheck.org. “The capacity to create false images is very high, but also there is a capacity to detect the images that is emerging very rapidly. The question is, will it emerge rapidly with enough capacity?”
Still, it’s not clear whether these websites are effective. Stanford University reported in a 2023 study that engagement with pink slime websites was “relatively low” and little evidence that living “in a news desert made people more likely to consume pink slime”.
The Philly Leader and the NW Arkansas News both only have links to Facebook accounts on their websites and have less than 450 followers on each. Meanwhile, the Copper Courier and Up North News have accounts on all the major platforms and a total of about 150,000 followers on Facebook.
Franklin said he thinks that a lot of people don’t actually click links on social media posts to visit the website.
“The goal of some of these operators is not to get traffic directly to their site, but it’s to go viral on social media,” he said.
Republican lawmakers and leaders of the conservative news sites the Daily Wire and the Federalist have also filed a lawsuit and launched investigations accusing NewsGuard of helping the federal government censor right-leaning media. The defense department hired the company strictly to counter “disinformation efforts by Russian, Chinese and Iranian government-linked operations targeting Americans and our allies”, Gordon Crovitz, the former Wall Street Journal publisher who co-founded NewsGuard, told the Hill in response to a House oversight committee investigation. “We look forward to clarifying the misunderstanding by the committee about our work for the Defense Department.”
To counter the flood of misinformation, social media companies must take a more active role in monitoring such content, according to Franklin and Skibinski.
“The biggest solution to this kind of site would be for the social media platforms to take more responsibility in terms of showing context to the user about sources that could be their own context. It could be data from third parties, like what we do,” said Skibinski.
Franklin would like to see a national media literacy campaign. States around the country have passed laws requiring such education in schools.
Franklin also hopes that legitimate local news could rebound. The MacArthur Foundation and other donors last year pledged $500m to help local outlets.
“I actually have more optimism now than I had a few years ago,” Franklin said. “We’re in the midst of historic changes in how people consume news and how it’s produced and how it’s distributed and how it’s paid for, but I think there’s still demand for local news, and that’s kind of where it all starts.”
Here lies the internet, murdered by generative AI
Corruption everywhere, even in YouTube's kids content
Erik Hoel Feb 27, 2024

Art for The Intrinsic Perspective is by Alexander Naughton
The amount of AI-generated content is beginning to overwhelm the internet. Or maybe a better term is pollute. Pollute its searches, its pages, its feeds, everywhere you look. I’ve been predicting that generative AI would have pernicious effects on our culture since 2019, but now everyone can feel it. Back then I called it the coming “semantic apocalypse.” Well, the semantic apocalypse is here, and you’re being affected by it, even if you don’t know it. A minor personal example: last year I published a nonfiction book, The World Behind the World, and now on Amazon I find this.
What, exactly, are these “workbooks” for my book? AI pollution. Synthetic trash heaps floating in the online ocean. The authors aren’t real people, some asshole just fed the manuscript into an AI and didn’t check when it spit out nonsensical summaries. But it doesn’t matter, does it? A poor sod will click on the $9.99 purchase one day, and that’s all that’s needed for this scam to be profitable since the process is now entirely automatable and costs only a few cents. Pretty much all published authors are affected by similar scams, or will be soon.
Now that generative AI has dropped the cost of producing bullshit to near zero, we see clearly the future of the internet: a garbage dump. Google search? They often lead with fake AI-generated images amid the real things. Post on Twitter? Get replies from bots selling porn. But that’s just the obvious stuff. Look closely at the replies to any trending tweet and you’ll find dozens of AI-written summaries in response, cheery Wikipedia-style repeats of the original post, all just to farm engagement. AI models on Instagram accumulate hundreds of thousands of subscribers and people openly shill their services for creating them. AI musicians fill up YouTube and Spotify. Scientific papers are being AI-generated. AI images mix into historical research. This isn’t mentioning the personal impact too: from now on, every single woman who is a public figure will have to deal with the fact that deepfake porn of her is likely to be made. That’s insane.
And rather than this being pure skullduggery, people and institutions are willing to embrace low-quality AI-generated content, trying to shift the Overton window to make things like this acceptable:

That’s not hardball capitalism. That’s polluting our culture for your own minor profit. It’s not morally legitimate for the exact same reasons that polluting a river for a competitive edge is not legitimate. Yet name-brand media outlets are embracing generative AI just like SEO-spammers are, for the same reasons.
E.g., investigative work at Futurism caught Sports Illustrated red-handed using AI-generated articles written by fake writers. Meet Drew Ortiz.
He doesn’t exist. That face is an AI-generated portrait, which was previously listed for sale on a website. As Futurism describes:
Ortiz isn't the only AI-generated author published by Sports Illustrated, according to a person involved with the creation of the content…
"At the bottom [of the page] there would be a photo of a person and some fake description of them like, 'oh, John lives in Houston, Texas. He loves yard games and hanging out with his dog, Sam.' Stuff like that," they continued. "It's just crazy."
This isn’t what everyone feared, which is AI replacing humans by being better—it’s replacing them because AI is so much cheaper. Sports Illustrated was not producing human-quality level content with these methods, but it was still profitable.
The AI authors' writing often sounds like it was written by an alien; one Ortiz article, for instance, warns that volleyball "can be a little tricky to get into, especially without an actual ball to practice with."
Sports Illustrated, in a classy move, deleted all the evidence. Drew was replace by Sora Tanaka, bearing a face also listed for sale on the same website with the description of a “joyful asian young-adult female with long brown hair and brown eyes.”
Given that even prestigious outlets like The Guardian refuse to put any clear limits on their use of AI, if you notice odd turns of phrase or low-quality articles, the likelihood that they’re written by an AI, or with AI-assistance, is now high.
Sadly, the people affected the most by generative AI are the ones who can’t defend themselves. Because they don’t even know what AI is. Yet we’ve abandoned them to swim in polluted information currents. I’m talking, unfortunately, about toddlers. Because let me introduce you to…
the hell that is AI-generated children’s YouTube content.
YouTube for kids is quickly becoming a stream of synthetic content. Much of it now consists of wooden digital characters interacting in short nonsensical clips without continuity or purpose. Toddlers are forced to sit and watch this runoff because no one is paying attention. And the toddlers themselves can’t discern that characters come and go and that the plots don’t make sense and that it’s all just incoherent dream-slop. The titles don’t match the actual content, and titles that are all the parents likely check, because they grew up in a culture where if a YouTube video said BABY LEARNING VIDEOS and had a million views it was likely okay. Now, some of the nonsense AI-generated videos aimed at toddlers have tens of millions of views.
Here’s a behind-the-scenes video on a single channel that made 1.2 million dollars via AI-generated “educational content” aimed at toddlers.
As the video says:
These kids, when they watch these kind of videos, they watch them over and over and over again.
They aren’t confessing. They’re bragging. And the particular channel they focus on isn’t even the worst offender—at least that channel’s content mostly matches the subheadings and titles, even if the videos are jerky, strange, off-putting, repetitious, clearly inhuman. Other channels, which are also obviously AI-generated, get worse and worse. Here’s a “kid’s education” channel that is AI-generated (took about one minute to find) with 11.7 million subscribers.
They don’t use proper English, and after quickly going through some shapes like the initial video title promises (albeit doing it in a way that makes you feel like you’re going insane) the rest of the video devolves into randomly-generated rote tasks, eerie interactions, more incorrect grammar, and uncanny musical interludes of songs that serve no purpose but to pad the time. It is the creation of an alien mind.
Here’s an example of the next frontier: completely start-to-finish AI-generated music videos for toddlers. Below is a how-to video for these new techniques. The result? Nightmarish parrots with twisted double-beaks and four mutated eyes singing artificial howls from beyond. Click and behold (or don’t, if you want to sleep tonight).
All around the nation there are toddlers plunked down in front of iPads being subjected to synthetic runoff, deprived of human contact even in the media they consume. There’s no other word but dystopian. Might not actual human-generated cultural content normally contain cognitive micro-nutrients (like cohesive plots and sentences, detailed complexity, reasons for transitions, an overall gestalt, etc) that the human mind actually needs? We’re conducting this experiment live. For the first time in history developing brains are being fed choppy low-grade and cheaply-produced synthetic data created en masse by generative AI, instead of being fed with real human culture. No one knows the effects, and no one appears to care. Especially not the companies, because…
OpenAI has happily allowed pollution.
Why blame them, specifically? Well, first of all, their massive impact—e.g., most of the kids videos are built from scripts generated by ChatGPT. And more generally, what AI capabilities are considered okay to deploy has long been a standard set by OpenAI. Despite their supposed safety focus, OpenAI failed to foresee that its creations would thoroughly pollute the internet across all platforms and services. You can see this failure in how they assessed potential negative outcomes in the announcement of GPT-2 on their blog, back in 2019. While they did warn that these models could have serious longterm consequences for the information ecosystem, the specifics they were concerned with were things like:
Generate misleading news articles
Impersonate others online
Automate the production of abusive or faked content to post on social media
Automate the production of spam/phishing content
This may sound kind of in line with what’s happened, but if you read further, it becomes clear that what they meant by “faked content” was mainly malicious actors promoting misinformation, or the same shadowy malicious actors using AI to phish for passwords, etc.
These turned out to be only minor concerns compared to AI’s cultural pollution. OpenAI kept talking about “actors” when they should have been talking about “users.” Because it turns out, all AI-generated content is fake! Or it’s all kind of fake. AI-written websites, now sprouting up like an unstoppable invasive species, don’t necessarily have an intent to mislead; it’s just that AI content is low-effort banalities generated for pennies, so you can SEO spam and do all sorts of manipulative games around search to attract eyeballs and ad revenue.
That is, the OpenAI team didn’t stop to think that regular users just generating mounds of AI-generated content on the internet would have very similar negative effects to as if there were a lot of malicious use by intentional bad actors. Because there’s no clear distinction! The fact that OpenAI was both honestly worried about negative effects, and at the same time didn’t predict the enshittification of the internet they spearheaded, should make us extremely worried they will continue to miss the negative downstream effects of their increasingly intelligent models. They failed to foresee the floating mounds of clickbait garbage, the synthetic info-trash cities, all to collect clicks and eyeballs—even from innocent children who don’t know any better. And they won’t do anything to stop it, because…
AI pollution is a tragedy of the commons.
This term, "tragedy of the commons,” originated in the rising environmentalism of the 20th century, and would lead to many of the regulations that keep our cities free of smog and our rivers clean. Garrett Hardin, an ecologist and biologist, coined it in an article in [Science](https://math.uchicago.edu/~shmuel/Modeling/Hardin, Tragedy of the Commons.pdf) in 1968. The article is still instructively relevant. Hardin wrote:
An implicit and almost universal assumption of discussions published in professional and semipopular scientific journals is that the problem under discussion has a technical solution…
He goes on to discuss several problems for which there are no technical solutions, since rational actors will drive the system toward destruction via competition:
The tragedy of the commons develops in this way. Picture a pasture open to all. It is to be expected that each herdsman will try to keep as many cattle as possible on the commons. Such an arrangement may work reasonably satisfactorily for centuries because tribal wars, poaching, and disease keep the numbers of both man and beast well below the carrying capacity of the land. Finally, however, comes the day of reckoning, that is, the day when the long-desired goal of social stability becomes a reality. At this point, the inherent logic of the commons remorselessly generates tragedy.
One central example of Hardin’s became instrumental to the environmental movement.
… the tragedy of the commons reappears in problems of pollution. Here it is not a question of taking something out of the commons, but of putting something in—sewage, or chemical, radioactive, and heat wastes into water; noxious and dangerous fumes into the air; and distracting and unpleasant advertising signs into the line of sight. The calculations of utility are much the same as before. The rational man finds that his share of the cost of the wastes he discharges into the commons is less than the cost of purifying his wastes before releasing them. Since this is true for everyone, we are locked into a system of "fouling our own nest," so long as we behave only as independent, rational, free-enterprisers.
We are currently fouling our own nests. Since the internet economy runs on eyeballs and clicks the new ability of anyone, anywhere, to easily generate infinite low-quality content via AI is now remorselessly generating tragedy.
The solution, as Hardin noted, isn’t technical. You can’t detect AI outputs reliably anyway (another initial promise that OpenAI abandoned). The companies won’t self regulate, given their massive financial incentives. We need the equivalent of a Clean Air Act: a Clean Internet Act. We can’t just sit by and let human culture end up buried.
Luckily we’re on the cusp of all that incredibly futuristic technology promised by AI. Any day now, our GDP will start to rocket forward. In fact, soon we’ll cure all disease, even aging itself, and have robot butlers and Universal Basic Income and high-definition personalized entertainment. Who cares if toddlers had to watch inhuman runoff for a few billion years of viewing-time to make the future happen? It was all worth it. Right? Let’s wait a little bit longer. If we wait just a little longer utopia will surely come.

We Need To Rewild The Internet
The internet has become an extractive and fragile monoculture. But we can revitalize it using lessons learned by ecologists.
By Maria Farrell and Robin Berjon April 16, 2024
“The word for world is forest” — Ursula K. Le Guin
In the late 18th century, officials in Prussia and Saxony began to rearrange their complex, diverse forests into straight rows of single-species trees. Forests had been sources of food, grazing, shelter, medicine, bedding and more for the people who lived in and around them, but to the early modern state, they were simply a source of timber.
So-called “scientific forestry” was that century’s growth hacking. It made timber yields easier to count, predict and harvest, and meant owners no longer relied on skilled local foresters to manage forests. They were replaced with lower-skilled laborers following basic algorithmic instructions to keep the monocrop tidy, the understory bare.
Information and decision-making power now flowed straight to the top. Decades later when the first crop was felled, vast fortunes were made, tree by standardized tree. The clear-felled forests were replanted, with hopes of extending the boom. Readers of the American political anthropologist of anarchy and order, James C. Scott, know [what happened](https://files.libcom.org/files/Seeing Like a State - James C. Scott.pdf) next.
It was a disaster so bad that a new word, Waldsterben, or “forest death,” was minted to describe the result. All the same species and age, the trees were flattened in storms, ravaged by insects and disease — even the survivors were spindly and weak. Forests were now so tidy and bare, they were all but dead. The first magnificent bounty had not been the beginning of endless riches, but a one-off harvesting of millennia of soil wealth built up by biodiversity and symbiosis. Complexity was the goose that laid golden eggs, and she had been slaughtered.
The story of German scientific forestry transmits a timeless truth: When we simplify complex systems, we destroy them, and the devastating consequences sometimes aren’t obvious until it’s too late.
That impulse to scour away the messiness that makes life resilient is what many conservation biologists call the “pathology of command and control.” Today, the same drive to centralize, control and extract has driven the internet to the same fate as the ravaged forests.
The internet’s 2010s, its boom years, may have been the first glorious harvest that exhausted a one-time bonanza of diversity. The complex web of human interactions that thrived on the internet’s initial technological diversity is now corralled into globe-spanning data-extraction engines making huge fortunes for a tiny few.
Our online spaces are not ecosystems, though tech firms love that word. They’re plantations; highly concentrated and controlled environments, closer kin to the industrial farming of the cattle feedlot or battery chicken farms that madden the creatures trapped within.
We all know this. We see it each time we reach for our phones. But what most people have missed is how this concentration reaches deep into the internet’s infrastructure — the pipes and protocols, cables and networks, search engines and browsers. These structures determine how we build and use the internet, now and in the future.
They’ve concentrated into a series of near-planetary duopolies. For example, as of April 2024, Google and Apple’s internet browsers have captured almost 85% of the world market share, Microsoft and Apple’s two desktop operating systems over 80%. Google runs 84% of global search and Microsoft 3%. Slightly more than half of all phones come from Apple and Samsung, while over 99% of mobile operating systems run on Google or Apple software. Two cloud computing providers, Amazon Web Services and Microsoft’s Azure [make up](https://www.hava.io/blog/2024-cloud-market-share-analysis-decoding-industry-leaders-and-trends#:~:text=Amazon Web Services (AWS) maintains,in the Asia-Pacific market.) over 50% of the global market. Apple and Google’s email clients manage nearly 90% of global email. Google and Cloudflare serve around 50% of global domain name system requests.
Two kinds of everything may be enough to fill a fictional ark and repopulate a ruined world, but can’t run an open, global “network of networks” where everyone has the same chance to innovate and compete. No wonder internet engineer Leslie Daigle termed the concentration and consolidation of the internet’s technical architecture “‘climate change’ of the Internet ecosystem.”
Walled Gardens Have Deep Roots
The internet made the tech giants possible. Their services have scaled globally, via its open, interoperable core. But for the past decade, they’ve also worked to enclose the varied, competing and often open-source or collectively provided services the internet is built on into their proprietary domains. Although this improves their operational efficiency, it also ensures that the flourishing conditions of their own emergence aren’t repeated by potential competitors. For tech giants, the long period of open internet evolution is over. Their internet is not an ecosystem. It’s a zoo.
Google, Amazon, Microsoft and Meta are consolidating their control deep into the underlying infrastructure through acquisitions, vertical integration, building proprietary networks, creating chokepoints and concentrating functions from different technical layers into a single silo of top-down control. They can afford to, using the vast wealth reaped in their one-off harvest of collective, global wealth.
“That impulse to scour away the messiness that makes life resilient is what many conservation biologists call the ‘pathology of command and control.’”
Taken together, the enclosure of infrastructure and imposition of technology monoculture forecloses our futures. Internet people like to talk about “the stack,” or the layered architecture of protocols, software and hardware, operated by different service providers that collectively delivers the daily miracle of connection. It’s a complicated, dynamic system with a basic value baked into the core design: Key functions are kept separate to ensure resilience, generality and create room for innovation.
Initially funded by the U.S. military and designed by academic researchers to function in wartime, the internet evolved to work anywhere, in any condition, operated by anyone who wanted to connect. But what was a dynamic, ever-evolving game of Tetris with distinct “players” and “layers” is today hardening into a continent-spanning system of compacted tectonic plates. Infrastructure is not just what we see on the surface; it’s the forces below, that make mountains and power tsunamis. Whoever controls infrastructure determines the future. If you doubt that, consider that in Europe we’re still using roads and living in towns and cities the Roman Empire mapped out 2,000 years ago.
In 2019, some internet engineers in the global standards-setting body, the Internet Engineering Task Force, raised the alarm. Daigle, a respected engineer who had previously chaired its oversight committee and internet architecture board, wrote in a policy brief that consolidation meant network structures were ossifying throughout the stack, making incumbents harder to dislodge and violating a core principle of the internet: that it does not create “permanent favorites.” Consolidation doesn’t just squeeze out competition. It narrows the kinds of relationships possible between operators of different services.
As Daigle put it: “The more proprietary solutions are built and deployed instead of collaborative open standards-based ones, the less the internet survives as a platform for future innovation.” Consolidation kills collaboration between service providers through the stack by rearranging an array of different relationships — competitive, collaborative — into a single predatory one.
Since then, standards development organizations started several initiatives to name and tackle infrastructure consolidation, but these floundered. Bogged down in technical minutiae, unable to separate themselves from their employers’ interests and deeply held professional values of simplification and control, most internet engineers simply couldn’t see the forest for the trees.
Up close, internet concentration seems too intricate to untangle; from far away, it seems too difficult to deal with. But what if we thought of the internet not as a doomsday “hyperobject,” but as a damaged and struggling ecosystem facing destruction? What if we looked at it not with helpless horror at the eldritch encroachment of its current controllers, but with compassion, constructiveness and hope?
Technologists are great at incremental fixes, but to regenerate entire habitats, we need to learn from ecologists who take a whole-systems view. Ecologists also know how to keep going when others first ignore you and then say it’s too late, how to mobilize and work collectively, and how to build pockets of diversity and resilience that will outlast them, creating possibilities for an abundant future they can imagine but never control. We don’t need to repair the internet’s infrastructure. We need to rewild it.
What Is Rewilding?
Rewilding “aims to restore healthy ecosystems by creating wild, biodiverse spaces,” according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature. More ambitious and risk-tolerant than traditional conservation, it targets entire ecosystems to make space for complex food webs and the emergence of unexpected interspecies relations. It’s less interested in saving specific endangered species. Individual species are just ecosystem components, and focusing on components loses sight of the whole. Ecosystems flourish through multiple points of contact between their many elements, just like computer networks. And like in computer networks, ecosystem interactions are multifaceted and generative.
Rewilding has much to offer people who care about the internet. As Paul Jepson and Cain Blythe wrote in their book “Rewilding: The Radical New Science of Ecological Recovery,” rewilding pays attention “to the emergent properties of interactions between ‘things’ in ecosystems … a move from linear to systems thinking.”
It’s a fundamentally cheerful and workmanlike approach to what can seem insoluble. It doesn’t micromanage. It creates room for “ecological processes [that] foster complex and self-organizing ecosystems.” Rewilding puts into practice what every good manager knows: Hire the best people you can, provide what they need to thrive, then get out of the way. It’s the opposite of command and control.
“The complex web of human interactions that thrived on the internet’s initial technological diversity is now corralled into globe-spanning data-extraction engines making huge fortunes for a tiny few.”
Rewilding the internet is more than a metaphor. It’s a framework and plan. It gives us fresh eyes for the wicked problem of extraction and control, and new means and allies to fix it. It recognizes that ending internet monopolies isn’t just an intellectual problem. It’s an emotional one. It answers questions like: How do we keep going when the monopolies have more money and power? How do we act collectively when they suborn our community spaces, funding and networks? And how do we communicate to our allies what fixing it will look and feel like?
Rewilding is a positive vision for the networks we want to live inside, and a shared story for how we get there. It grafts a new tree onto technology’s tired old stock.
What Ecology Knows
Ecology knows plenty about complex systems that technologists can benefit from. First, it knows that shifting baselines are real.
If you were born around the 1970s, you probably remember many more dead insects on the windscreen of your parents’ car than on your own. Global land-dwelling insect populations are dropping about 9% a decade. If you’re a geek, you probably programmed your own computer to make basic games. You certainly remember a web with more to read than the same five websites. You may have even written your own blog.
But many people born after 2000 probably think a world with few insects, little ambient noise from birdcalls, where you regularly use only a few social media and messaging apps (rather than a whole web) is normal. As Jepson and Blythe wrote, shifting baselines are “where each generation assumes the nature they experienced in their youth to be normal and unwittingly accepts the declines and damage of the generations before.” Damage is already baked in. It even seems natural.
Ecology knows that shifting baselines dampen collective urgency and deepen generational divides. People who care about internet monoculture and control are often told they’re nostalgists harkening back to a pioneer era. It’s fiendishly hard to regenerate an open and competitive infrastructure for younger generations who’ve been raised to assume that two or three platforms, two app stores, two operating systems, two browsers, one cloud/mega-store and a single search engine for the world comprise the internet. If the internet for you is the massive sky-scraping silo you happen to live inside and the only thing you can see outside is the single, other massive sky-scraping silo, then how can you imagine anything else?
Concentrated digital power produces the same symptoms that command and control produces in biological ecosystems; acute distress punctuated by sudden collapses once tipping points are reached. What scale is needed for rewilding to succeed? It’s one thing to reintroduce wolves to the 3,472 square miles of Yellowstone, and quite another to cordon off about 20 square miles of a polder (land reclaimed from a body of water) known as Oostvaardersplassen near Amsterdam. Large and diverse Yellowstone is likely complex enough to adapt to change, but Oostvaardersplassen has struggled.
“Our online spaces are not ecosystems, though tech firms love that word. They’re plantations; highly concentrated and controlled environments … that madden the creatures trapped within.”
In the 1980s, the Dutch government attempted to regenerate a section of the overgrown Oostvaardersplassen. An independent-minded government ecologist, Frans Vera, said reeds and scrub would dominate unless now-extinct herbivores grazed them. In place of ancient aurochs, the state forest management agency introduced the famously bad-tempered German Heck cattle and in place of an extinct steppe pony, a Polish semi-feral breed.
Some 30 years on, with no natural predators, and after plans for a wildlife corridor to another reserve came to nothing, there were many more animals than the limited winter vegetation could sustain. People were horrified by starving cows and ponies, and beginning in 2018, government agencies instituted animal welfare checks and culling.
Just turning the clock back was insufficient. The segment of Oostvaardersplassen was too small and too disconnected to be rewilded. Because the animals had nowhere else to go, overgrazing and collapse was inevitable, an embarrassing but necessary lesson. Rewilding is a work in progress. It’s not about trying to revert ecosystems to a mythical Eden. Instead, rewilders seek to rebuild resilience by restoring autonomous natural processes and letting them operate at scale to generate complexity. But rewilding, itself a human intervention, can take several turns to get right.
Whatever we do, the internet isn’t returning to old-school then-common interfaces like FTP and Gopher, or organizations operating their own mail servers again instead of off-the-shelf solutions like G-Suite. But some of what we need is already here, especially on the web. Look at the resurgence of RSS feeds, email newsletters and blogs, as we discover (yet again) that relying on one app to host global conversations creates a single point of failure and control. New systems are growing, like the Fediverse with its federated islands, or Bluesky with algorithmic choice and composable moderation.
We don’t know what the future holds. Our job is to keep open as much opportunity as we can, trusting that those who come later will use it. Instead of setting purity tests for which kind of internet is most like the original, we can test changes against the values of the original design. Do new standards protect the network’s “generality,” i.e. its ability to support multiple uses, or is functionality limited to optimize efficiency for the biggest tech firms?
As early as 1985, plant ecologists Steward T.A. Pickett and Peter S. White wrote in “The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics,” that an “essential paradox of wilderness conservation is that we seek to preserve what must change.” Some internet engineers know this. David Clark, a Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor who worked on some of the internet’s earliest protocols, wrote an entire book about other network architectures that might have been built if different values, like security or centralized management, had been prioritized by the internet’s creators.
But our internet took off because it was designed as a general-purpose network, built to connect anyone.
Our internet was built to be complex and unbiddable, to do things we cannot yet imagine. When we interviewed Clark, he told us that “‘complex’ implies a system in which you have emergent behavior, a system in which you can’t model the outcomes. Your intuitions may be wrong. But a system that’s too simple means lost opportunities.” Everything we collectively make that’s worthwhile is complex and thereby a little messier. The cracks are where new people and ideas get in.
Internet infrastructure is a degraded ecosystem, but it’s also a built environment, like a city. Its unpredictability makes it generative, worthwhile and deeply human. In 1961, Jane Jacobs, an American-Canadian activist and author of “The Death and Life of Great American Cities,” argued that mixed-use neighborhoods were safer, happier, more prosperous, and more livable than the sterile, highly controlling designs of urban planners like New York’s Robert Moses.
“As a top-down, built environment, the internet has become something that is done to us, not something we collectively remake every day.”
Just like the crime-ridden, Corbusier-like towers Moses crammed people into when he demolished mixed-use neighborhoods and built highways through them, today’s top-down, concentrated internet is, for many, an unpleasant and harmful place. Its owners are hard to remove, and their interests do not align with ours.
As Jacobs wrote: “As in all Utopias, the right to have plans of any significance belonged only to the planners in charge.” As a top-down, built environment, the internet has become something that is done to us, not something we collectively remake every day.
Ecosystems endure because species serve as checks and balances on each other. They have different modes of interaction, not just extraction, but mutualism, commensalism, competition and predation. In flourishing ecosystems, predators are subject to limits. They’re just one part of a complex web that passes calories around, not a one-way ticket to the end of evolution.
Ecologists know that diversity is resilience.
On July 18, 2001, 11 carriages of a 60-car freight train derailed in the Howard Street Tunnel under Mid-Town Belvedere, a neighborhood just north of downtown Baltimore. Within minutes, one carriage containing a highly flammable chemical was punctured. The escaping chemical ignited, and soon, adjacent carriages were alight in a fire that took about five days to put out. The disaster multiplied and spread. Thick, brick tunnel walls acted like an oven, and temperatures rose to nearly 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. A more than three-foot-wide water main above the tunnels burst, flooding the tunnel with millions of gallons within hours. It only cooled a little. Three weeks later, an explosion linked to the combustible chemical blew out manhole covers located as far as two miles away.
WorldCom, then the second largest long-distance phone company in the U.S., had fiber-optic cables in the tunnel carrying high volumes of phone and internet traffic. However, according to Clark, the MIT professor, WorldCom’s resilience planning meant traffic was spread over different fiber networks in anticipation of just this kind of event.
On paper, WorldCom had network redundancy. But almost immediately, U.S. internet traffic slowed, and WorldCom’s East Coast and transatlantic phone lines went down. The region’s narrow physical topography had concentrated all those different fiber networks into a single chokepoint, the Howard Street Tunnel. WorldCom’s resilience was, quite literally, incinerated. It had technological redundancy, but not diversity. Sometimes we don’t notice concentration until it’s too late.
Clark tells the story of the Howard Street Tunnel fire to show that bottlenecks aren’t always obvious, especially at the operational level, and huge systems that seem secure, due to their size and resources, can unexpectedly crumble.
In today’s internet, much traffic passes through tech firms’ private networks, for example, Google and Meta’s own undersea cables. Much internet traffic is served from a few dominant content distribution networks, like Cloudflare and Akamai, who run their own networks of proxy servers and data centers. Similarly, that traffic goes through an increasingly small number of domain name system (DNS) resolvers, which work like phone books for the internet, linking website names to their numeric address.
All of this improves network speed and efficiency but creates new and non-obvious bottlenecks like the Howard Street Tunnel. Centralized service providers say they’re better resourced and skilled at attacks and failures, but they are also large, attractive targets for attackers and possible single points of system failure.
On Oct. 21, 2016, dozens of major U.S. websites suddenly stopped working. Domain names belonging to Airbnb, Amazon, PayPal, CNN and The New York Times simply didn’t resolve. All were clients of the commercial DNS service provider, Dyn, which had been hit by a cyberattack. Hackers infected [tens of thousands](https://coverlink.com/case-study/mirai-ddos-attack-on-dyn/#:~:text=Impacted internet platforms included PayPal,platforms in approximately two hours) of internet-enabled devices with malicious software, creating a network of hijacked devices, or a botnet, that they used to bombard Dyn with queries until it collapsed. America’s biggest internet brands were brought down by nothing more than a network of baby monitors, security webcams and other consumer devices. Although they all likely had resilience planning and redundancies, they went down because a single chokepoint — in one crucial layer of infrastructure — failed.
“Crashes, fires and floods may simply be entropy in action, but systemically concentrated and risky infrastructures are choices made manifest — and we can make better ones.”
Widespread outages due to centralized chokepoints have become so common that investors even use them to identify opportunities. When a failure by cloud provider Fastly took high-profile websites offline in 2021, its share price surged. Investors were delighted by headlines that informed them of an obscure technical service provider with an apparent lock on an essential service. To investors, this critical infrastructure failure doesn’t look like fragility but like a chance to profit.
The result of infrastructural narrowness is baked-in fragility that we only notice after a breakdown. But monoculture is also highly visible in our search and browser tools. Search, browsing and social media are how we find and share knowledge and how we communicate. They’re a critical, global epistemic and democratic infrastructure, controlled by just a few U.S. companies. Crashes, fires and floods may simply be entropy in action, but systemically concentrated and risky infrastructures are choices made manifest — and we can make better ones.
The Look & Feel Of A Rewilded Internet
A rewilded internet will have many more service choices. Some services like search and social media will be broken up, as AT&T eventually was. Instead of tech firms extracting and selling people’s personal data, different payment models will fund the infrastructure we need. Right now, there is little explicit provision for public goods like internet protocols and browsers, essential to making the internet work. The biggest tech firms subsidize and profoundly influence them.
Part of rewilding means taking what’s been pulled into the big tech stack back out of it, and paying for the true costs of connectivity. Some things like basic connectivity we will continue to pay for directly, and others, like browsers, we will support indirectly but transparently, as described below. The rewilded internet will have an abundance of ways to connect and relate to each other. There won’t be just one or two numbers to call if leaders of a political coup decide to shut the internet down in the middle of the night, as has happened in places like Egypt and Myanmar. No one entity will permanently be on top. A rewilded internet will be a more interesting, usable, stable and enjoyable place to be.
Through extensive research, Nobel-winning economist Elinor Ostrom found that “when individuals are well informed about the problem they face and about who else is involved, and can build settings where trust and reciprocity can emerge, grow, and be sustained over time, costly and positive actions are frequently taken without waiting for an external authority to impose rules, monitor compliance, and assess penalties.” Ostrom found people spontaneously organizing to manage natural resources — from water company cooperation in California to Maine lobster fishermen organizing to prevent overfishing.
Self-organization also exists as part of a key internet function: traffic coordination. Internet exchange points (IXPs) are an example of common-pool resource management, where internet service providers (ISPs) collectively agree to carry each other’s data for low or no cost. Network operators of all kinds — telecoms companies, large tech firms, universities, governments and broadcasters — all need to send large amounts of data through other ISPs’ networks so that it gets to its destination.
If they managed this separately through individual contracts, they’d spend much more time and money. Instead, they often form IXPs, typically as independent, not-for-profit associations. As well as managing traffic, IXPs have, in many — and especially developing — countries, formed the backbone of a flourishing technical community that further drives economic development.
Both between people and on the internet, connections are generative. From technical standards to common-pool resource management and even to more localized broadband networks known as “altnets,” internet rewilding already has a deep toolbox of collective action ready to be deployed.
The New Drive For Antitrust & Competition
The list of infrastructures to be diversified is long. As well as pipes and protocols, there are operating systems, browsers, search engines, the Domain Name System, social media, advertising, cloud providers, app stores, AI companies and more. And these technologies also intertwined.
But showing what can be done in one area creates opportunities in others. First, let’s start with regulation.
You don’t always need a big new idea like rewilding to frame and motivate major structural change. Sometimes reviving an old idea will do. President Biden’s 2021 “Executive Order on Promoting Competition in the American Economy” revived the original, pro-worker, trust-busting scope and urgency of the early 20th-century legal activist and Supreme Court Justice Louis D. Brandeis, along with rules and framings that date back to before the 1930s New Deal.
“Rewilding an already built environment isn’t just sitting back and seeing what tender, living thing can force its way through the concrete. It’s razing to the ground the structures that block out light for everyone not rich enough to live on the top floor.”
U.S. antitrust law was created to break the power of oligarchs in oil, steel and railroads who threatened America’s young democracy. It gave workers basic protections and saw equal economic opportunity as essential to freedom. This view of competition as essential was whittled away by Chicago School economic policies in the 1970s and Reagan-era judges’ court rulings over the decades. They believed intervention should only be permitted when monopoly power causes consumer prices to rise. The intellectual monoculture of that consumer-harm threshold has since spread globally.
It’s why governments just stood aside as 21st-century tech firms romped to oligopoly. If a regulator’s sole criterion for action is to make sure consumers don’t pay a penny more, then the free or data-subsidized services of tech platforms don’t even register. (Of course, consumers pay in other ways, as these tech giants exploit their personal information for profit.) This laissez-faire approach allowed the biggest firms to choke off competition by acquiring their competitors and vertically integrating service providers, creating the problems we have today.
Regulators and enforcers in Washington and Brussels now say they have learned that lesson and won’t allow AI dominance to happen as internet concentration did. Federal Trade Commission Chair Lina Khan and U.S. Department of Justice antitrust enforcer, Jonathan Kanter, are identifying chokepoints in the AI “stack” — concentration in control of processing chips, datasets, computing capacity, algorithm innovation, distribution platforms and user interfaces — and analyzing them to see if they affect systemic competition. This is potentially good news for people who want to prevent the current dominance of tech giants being grandfathered into our AI future.
In his 2021 signing of the executive order on competition, President Biden said: “Capitalism without competition isn’t capitalism; it’s exploitation.” Biden’s enforcers are changing the kinds of cases they take up and widening the applicable legal theories on harm that they bring to judges. Instead of the traditionally narrow focus on consumer prices, today’s cases argue that the economic harms perpetrated by dominant firms include those suffered by their workers, small companies and the market as a whole.
Khan and Kanter have jettisoned narrow and abstruse models of market behavior for real-world experiences of healthcare workers, farmers and writers. They get that shutting off economic opportunity fuels far-right extremism. They’ve made antitrust enforcement and competition policy explicitly about coercion versus choice, power versus democracy. Kanter told a recent conference in Brussels that “excessive concentration of power is a threat … it’s not just about prices or output but it’s about freedom, liberty and opportunity.”
Enforcers in Washington and Brussels are starting to preemptively block tech firms from using dominance in one realm to take over another. After scrutiny by the U.S. FTC and European Commission, Amazon recently abandoned its plan to acquire the home appliance manufacturer, iRobot. Regulators on both sides of the Atlantic have also moved to stop Apple from using its iPhone platform dominance to squeeze app store competition and dominate future markets through, for example, pushing the usage of CarPlay on automakers and limiting access to its tap-to-pay digital wallet in the financial services sector.
Still, so far, their enforcement actions have focused on the consumer-facing, highly visible parts of the tech giants’ exploitative and proprietary internet. The few, narrow measures of the 2021 executive order that aim to reduce infrastructure-based monopolies, only prevent future abuses like radio spectrum-hogging, not those already locked in. Sure, the best way to deal with monopolies is to stop them from happening in the first place. But unless regulators and enforcers eradicate the existing dominance of these giants now, we’ll be living in today’s infrastructure monopoly for decades, perhaps even a century.
Even activist regulators have shied away from applying the toughest remedies for concentration in long-consolidated markets, such as non-discrimination requirements, functional interoperability and structural separations, i.e. breaking companies up. And declaring that search and social media monopolies are actually public utilities — and forcing them to act as common carriers open to all — is still too extreme for most.
But rewilding a built environment isn’t just sitting back and seeing what tender, living thing can force its way through the concrete. It’s razing to the ground the structures that block out light for everyone not rich enough to live on the top floor.
“Ecologists have reoriented their field as a ‘crisis discipline,’ a field of study that’s not just about learning things but about saving them. We technologists need to do the same.”
When the writer and activist Cory Doctorow wrote about how to free ourselves from the clutches of Big Tech, he said that though breaking up big companies will likely take decades, providing strong and mandatory interoperability would open up innovative space and slow the flow of money to the largest firms — money they would otherwise use to deepen their moats.
Doctorow describes “comcom,” or competitive compatibility, as a kind of “guerrilla interoperability, achieved through reverse engineering, bots, scraping and other permissionless tactics.” Before a thicket of invasive laws sprung up to strangle it, comcom was how people figured out how to fix cars and tractors or re-write software. Comcom drives the try-every-tactic-until-one-works behavior you see in a flourishing ecosystem.
In an ecosystem, diversity of species is another way of saying “diversity of tactics,” as each successful new tactic creates a new niche to occupy. Whether it’s an octopus camouflaging itself as a sea snake, a cuckoo smuggling her chicks into another bird’s nest, orchids producing flowers that look just like a female bee, or parasites influencing rodent hosts to take life-ending risks, each evolutionary micro-niche is created by a successful tactic. Comcom is simply tactical diversity; it’s how organisms interact in complex, dynamic systems. And humans have demonstrated the epitome of short-term thinking by enabling the oligarchs who are trying to end it.
Efforts are underway. The EU already has several years of experience with interoperability mandates and precious insight into how determined firms work to circumvent such laws. The U.S., however, is still in its early days of ensuring software interoperability, for example, for videoconferencing.
Perhaps one way to motivate and encourage regulators and enforcers everywhere is to explain that the subterranean architecture of the internet has become a shadowland where evolution has all but stopped. Regulators’ efforts to make the visible internet competitive will achieve little unless they also tackle the devastation that lies beneath.
Next Steps
Much of what we need is already here. Beyond regulators digging deep for courage, vision and bold new litigation strategies, we need vigorous, pro-competitive government policies around procurement, investments and physical infrastructure. Universities must reject research funding from tech firms because it always comes with conditions, both spoken and unspoken.
Instead, we need more publicly funded tech research with publicly released findings. Such research should investigate power concentration in the internet ecosystem and practical alternatives to it. We need to recognize that much of the internet’s infrastructure is a de facto utility that we must regain control of.
We must ensure regulatory and financial incentives and support for alternatives including common-pool resource management, community networks, and the myriad other collaborative mechanisms people have used to provide essential public goods like roads, defense and clean water.
All this takes money. Governments are starved of tax revenue by the once-in-history windfalls seized by today’s tech giants, so it’s clear where the money is. We need to get it back.
We know all this, but still find it so hard to collectively act. Why?
Herded into rigid tech plantations rather than functioning, diverse ecosystems, it’s tough to imagine alternatives. Even those who can see clearly may feel helpless and alone. Rewilding unites everything we know we need to do and brings with it a whole new toolbox and vision.
Ecologists face the same systems of exploitation and are organizing urgently, at scale and across domains. They see clearly that the issues aren’t isolated but are instances of the same pathology of command and control, extraction and domination that political anthropologist Scott first noticed in scientific forestry. The solutions are the same in ecology and technology: aggressively use the rule of law to level out unequal capital and power, then rush in to fill the gaps with better ways of doing things.
Keep The Internet, The Internet
Susan Leigh Star, a sociologist and theorist of infrastructure and networks, wrote in her 1999 influential paper, “The Ethnography of Infrastructure”:
“Study a city and neglect its sewers and power supplies (as many have), and you miss essential aspects of distributional justice and planning power. Study an information system and neglect its standards, wires, and settings, and you miss equally essential aspects of aesthetics, justice, and change.”
The technical protocols and standards that underlie the internet’s infrastructure are ostensibly developed in open, collaborative standards development organizations (SDOs), but are also increasingly under the control of a few companies. What appear to be “voluntary” standards are often the business choices of the biggest firms.
The dominance of SDOs by big firms also shapes what does not get standardized — for example, search, which is effectively a global monopoly. While efforts to directly address internet consolidation have been raised repeatedly within SDOs, little progress has been made. This is damaging SDOs’ credibility, especially outside the U.S. SDOs must radically change or they will lose their implicit global mandate to steward the future of the internet.
We need internet standards to be global, open and generative. They’re the wire models that give the internet its planetary form, the gossamer-thin but steely-strong threads holding together its interoperability against fragmentation and permanent dominance.
*Make Laws & Standards Work Together*
In 2018, a small group of Californians maneuvered the Legislature into passing the [California Consumer Privacy Act](https://oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa#:~:text=The California Consumer Privacy Act,how to implement the law.). Nested in the statute was an unassuming provision, the “right to opt out of sale or sharing” your personal information via a “user-enabled global privacy control” or GPC signal that would create an automated method for doing so. The law didn’t define how GPC would work. Because a technical standard was required for browsers, businesses and providers to speak the same language, the signal’s details were delegated to a group of experts.
In July 2021, California’s attorney general mandated that all businesses use the newly created GPC for California-based consumers visiting their websites. The group of experts is now shepherding the technical specification through global web standards development at the World Wide Web Consortium. For California residents, GPC automates the request to “accept” or “reject” sales of your data, such as cookie-based tracking, on its websites. However, it isn’t yet supported by major default browsers like Chrome and Safari. Broad adoption will take time, but it’s a small step in changing real-world outcomes by driving antimonopoly practices deep into the standards stack — and it’s already being [adopted](https://usercentrics.com/knowledge-hub/what-is-global-privacy-control/#:~:text=United States and state-level laws and GPC,-Six new data&text=The laws in California%2C Connecticut,to respect Global Privacy Control.) elsewhere.
GPC is not the first legally mandated open standard, but it was deliberately designed from day one to bridge policymaking and standards-setting. The idea is gaining ground. A recent United Nations Human Rights Council report recommends that states delegate “regulatory functions to standard-setting organizations.”
Make Service-Providers — Not Users — Transparent
Today’s internet offers minimal transparency of key internet infrastructure providers. For example, browsers are highly complex pieces of infrastructure that determine how billions of people use the web, yet they are provided for free. That’s because the most commonly used search engines enter into opaque financial deals with browsers, paying them to be set as the default. Since few people change their default search engine, browsers like Safari and Firefox make money by defaulting the search bar to Google, locking in its dominance even as the search engine’s quality of output declines.
This creates a quandary. If antitrust enforcers were to impose competition, browsers would lose their main source of income. Infrastructure requires money, but the planetary nature of the internet challenges our public funding model, leaving the door open to private capture. However, if we see the current opaque system as what it is, a kind of non-state taxation, then we can craft an alternative.
Search engines are a logical place for governments to mandate the collection of a levy that supports browsers and other key internet infrastructure, which could be financed transparently under open, transnational, multistakeholder oversight.
Make Space To Grow
We need to stop thinking of internet infrastructure as too hard to fix. It’s the underlying system we use for nearly everything we do. The former prime minister of Sweden, Carl Bildt, and former Canadian deputy foreign minister, Gordon Smith, wrote in 2016 that the internet was becoming “the infrastructure of all infrastructure.” It’s how we organize, connect and build knowledge, even — perhaps — planetary intelligence. Right now, it’s concentrated, fragile and utterly toxic.
Ecologists have reoriented their field as a “crisis discipline,” a field of study that’s not just about learning things but about saving them. We technologists need to do the same. Rewilding the internet connects and grows what people are doing across regulation, standards-setting and new ways of organizing and building infrastructure, to tell a shared story of where we want to go. It’s a shared vision with many strategies. The instruments we need to shift away from extractive technological monocultures are at hand or ready to be built.
Amazon buys nuclear-powered data centre from Talen
US-based Talen Energy Corporation has sold its Cumulus data centre campus in Pennsylvania to Amazon subsidiary Amazon Web Services (AWS) for $650m. This includes a long-term agreement to provide power from Talen's Susquehanna NPP. The 2,500 MWe adjacent Susquehanna Steam Electric Station currently supplies power to the data centre.
13 March 2024
The $650m will be paid in stages – $350m on closing and $300m to be released on the attainment of development milestones later this year. Talen will also receive additional revenue from AWS related to sales of Susquehanna's energy to the grid.
“We believe this is a transformative transaction with long term benefits,” said Talen President & CEO Mark “Mac” McFarland, in a call with investors and media. As power demand continues to rise worldwide, “data centres are at the heart of that growth,” he noted.
Texas-based Talen is the majority owner and operator of the Susquehanna plant with 90% owned and operated by Talen subsidiary Susquehanna Nuclear. Allegheny Electric owns the other 10%. The plant’s two General Electric boiling water reactors began operation in 1983 and are licensed to operate until 2042 and 2044. In 2022, Talen filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy as part of a financial restructuring, exiting bankruptcy in 2023. The transaction with AWS is expected to boost to its cash flow. After paying off debts, interest and other costs, Talen expects net proceeds of $361m from the deal.
The Cumulus campus is directly connected to the NPP. The data centre's four substations have a total potential 960 MW of redundant capacity. This includes 200 MW currently associated with the Nautilus cryptocurrency facility, in which Talen will retain its 75% interest. A further 240 MW of redundant capacity for data centres is expected to be ready this year. The campus has a "robust and redundant" fibre network.
According to Talen Energy’s investor presentation, it will supply fixed-price nuclear power to AWS’s new data centre as it is built. AWS has minimum contractual power commitments increasing in 120 MW increments over several years. AWS has a one-time option to cap commitments at 480 MW and two 10-year extension options tied to nuclear licence renewals.
"Power demand is growing for the first time in years, and AI and data centres are at the heart of that growth," McFarland said. "Data from the International Energy Agency suggests that energy demand from data centres, AI and cryptocurrencies could more than double over the next three years."
He added that the transaction will benefit the wider community by creating jobs and catalysing economic development as well as strengthening the Susquehanna plant itself as a major employer and significant taxpayer.

En Chine, Internet est en train de disparaître
« Si Internet est l'avenir de la civilisation, alors notre génération n’aura pas d'histoire — parce qu'Internet n'aura laissé de nous aucune trace. » On a longtemps cru qu’Internet serait la plus puissante des bibliothèques. La mémoire exhaustive de l’humanité. Le web chinois, dont les contenus sont désormais davantage produits et consommés depuis des téléphones, démontre le contraire : Internet n’archive rien. He Jiayan dissèque une révolution aux conséquences aussi violentes que souterraines.
2 juin 2024 • Numérique Auteur Le Grand Continent
« Nous avons longtemps conçu Internet comme une mémoire — nous ne savions pas que c’était celle d’un poisson rouge. » En une décennie, alors même qu’il devenait de plus en plus universel par son nombre d’utilisateurs, Internet a perdu plus d’un tiers de son contenu.
Pour la Chine, cet effondrement archivistique est encore plus important. He Jiayan, journaliste chinois spécialisé dans le web et le secteur des nouvelles technologies, travaille à partir d’archives informatiques datant d’avant l’Internet mobile. Il montre que le durcissement politique chinois est loin d’être le premier facteur de la disparition de pans entiers du web. L’autocensure et la course à la rentabilité ont conduit souterrainement à la disparition d’une quantité énorme d’informations des serveurs. À l’heure où l’Internet mobile semble être en train de remplacer le premier âge d’Internet, cette disparition semble peu visible — elle est pour autant tout à fait réelle.
Au-delà de la dimension technique, Jiayan alerte sur la disparition d’une mémoire commune constitutive d’une culture populaire encore vivante, confiée à des serveurs qu’on croyait immortels — et qui menace aujourd’hui de s’effondrer. Pour toute une génération qui a immatériellement construit sa vie dans l’Internet des vingt premières années du XXIe siècle, le risque très concret est de se retrouver avec deux décennies sans mémoire.
Commençons par une petite expérience.
He Jiayan
Si l’on cherche « Jack Ma » sur Baidu et qu’on fixe une période de référence courant de 1998 à 2005, combien d’informations apparaîtront ? Plutôt 100 millions, 10 millions ou 1 million ?
J’ai posé la question à plusieurs groupes et l’opinion majoritaire considère toujours que l’ordre de grandeur se situerait entre quelques millions et quelques dizaines de millions. Après tout, Internet est si vaste. Jack Ma, l’ancien entrepreneur haut en couleur, a dû y laisser beaucoup de traces.
En réalité, pour une recherche Baidu sélectionnant la plage de dates « 22 mai 1998 à 22 mai 2005 », le total des résultats contenant l’expression « Jack Ma » s’élève à 1.
Et ce seul résultat est lui-même faux : en cliquant dessus, on constate que l’article a en fait été publié en 2021, c’est-à-dire en dehors de la période délimitée ci-dessus. S’il apparaît dans notre recherche, ce n’est que de manière inexplicable.
En d’autres termes, si l’on veut connaître les expériences de Jack Ma, ses relations, les discussions à son sujet, ses discours ou l’histoire de son entreprise Alibaba pendant cette période, la quantité d’informations brutes valables qu’on obtient sur Internet est nulle.
Pour une recherche Baidu sélectionnant la plage de dates « 22 mai 1998 à 22 mai 2005 », le total des résultats contenant l’expression « Jack Ma » s’élève à 1.
He Jiayan
Peut-être est-ce un problème de Baidu ? Peut-être qu’en utilisant Bing ou Google, la recherche est davantage probante ?
J’ai essayé : ces deux sites affichent bien des résultats valides — un peu plus que Baidu — mais seulement une petite dizaine. Il y a aussi davantage de résultats invalides qui n’entrent pas dans la période sélectionnée — probablement pour une raison purement technique.
On peut alors se demander si ce n’est pas parce que Jack Ma est controversé en Chine que ces résultats ne sont pas consultables.
Ce serait vrai si c’était seulement le cas de Jack Ma. Mais j’ai aussi fait des recherches pour la même période sur Ma Huateng, Lei Jun, Ren Zhengfei, et même Luo Yonghao et Sister Fu Rong — qui étaient à l’époque des célébrités sur Internet — ou encore Jay Chou, Li Yuchun — qui étaient alors des stars de la musique. Les résultats sont du même ordre.
He Jiayan cite des hommes d’affaires chinois célèbres faisant partie des BATX, l’équivalent des GAFA chinois : Jack Ma est le fameux fondateur d’Alibaba, disparu soudainement est désormais exilé hors de Chine ; Ren Zhengfei est le fondateur et PDG de Huawei Technologies ; Ma Huateng, celui de Tencent Holdings ; et Lei Jun, le fondateur de Xiaomi. Lyo Yonghao et Sister Fu Rong sont des blogueurs célèbres en Chine dans les années 2000.
Dans le cas de la recherche sur Lei Jun, après avoir testé différents sites web, différents noms de personnes et différentes périodes, j’ai découvert un phénomène étonnant. Presque toutes les archives des sites web chinois qui étaient populaires à l’époque — tels que NetEase, Sohu, SMTH BBS, Xizi Hutong, Keyhole Forum, Tianya Club, RenRen Network, Sina Blogs, Baidu Tieba — ont disparu. Un grand nombre de contenus sur des sites web personnels ont également disparu sur une période ancienne, et la plupart des sites web ont même disparu pour toutes les périodes. La seule exception est Sina.com, où l’on peut encore trouver des informations datant de plus de dix ans — mais en nombre assez limité. Plus de 99,9999 % du contenu a disparu.
Nous avons longtemps conçu Internet comme une mémoire — nous ne savions pas que c’était celle d’un poisson rouge.
He Jiayan
Nous sommes en train de passer à côté d’un problème préoccupant : l’Internet chinois s’effondre de manière inéluctable — et le contenu qui existait avant l’émergence de l’Internet mobile a aujourd’hui presque complètement disparu.
Nous avons longtemps conçu Internet comme une mémoire — nous ne savions pas que c’était celle d’un poisson rouge.
Au cours des deux dernières années, je me suis forgé une conviction très claire : le nombre d’informations que l’on peut trouver en ligne se réduit chaque année à une vitesse vertigineuse. Il n’y a pas si longtemps, je pouvais encore trouver certaines sources originales. C’est progressivement devenu impossible. Je pouvais encore découvrir les discours des protagonistes ou les articles qu’ils avaient écrits — puis je ne les ai plus trouvés. Je pouvais encore voir de nombreuses interviews ou des vidéos en ligne — elles ont été effacées progressivement.
Au cours des deux dernières années, je me suis forgé une conviction très claire : le nombre d’informations que l’on peut trouver en ligne se réduit chaque année à une vitesse vertigineuse.
He Jiayan
Tout se passe comme si un monstre d’un nouveau genre était apparu, qui dévore les pages web tout au long de l’histoire, les avalant du passé vers le présent, d’abord par petites bouchées, puis par grandes bouchées, dévorant tout l’Internet chinois — cinq ans par-ci, dix ans par là.
Lorsque l’on regardera en arrière, on constatera que tout ce qui existait dans l’Internet chinois avant la création du mobile — qu’il s’agisse d’un portail, du site officiel d’une organisation, d’une page web personnelle, de forums publics, des blogs Sina, de posts Baidu, de documents, de photos, de musique, de vidéos, etc. — aura disparu.
Je me souviens qu’il y a plus de dix ans, j’avais l’habitude de changer d’ordinateur parce que mes photos et mes articles compressés étaient stockées sur un serveur. Quelques années plus tard, j’ai découvert que l’entièreté du serveur avait disparu. J’avais l’habitude d’utiliser hotmail, et puis tout a disparu. J’ai également écrit des messages sur RenRen et MySpace… tous disparus.
Tout se passe comme si un monstre d’un nouveau genre était apparu, qui dévore les pages web tout au long de l’histoire.
He Jiayan
Nous pensions qu’Internet pouvait tout sauvegarder. Il s’est avéré qu’il ne peut rien garder.
Pourquoi cela s’est-il produit ?
Je pense qu’il y a deux raisons principales.
La première est d’ordre économique.
Un site Internet nécessite de la bande passante, une salle de serveurs, du personnel pour le gérer et l’entretenir, ainsi qu’une quantité non négligeable de coûts réglementaires et d’entretien divers. S’il existe une valeur stratégique — par exemple, informer de ses activités pour une entreprise — ou une valeur de trafic à court terme — par exemple, s’il y a toujours des gens qui viennent voir le site de temps en temps —, et si en même temps les comptes de l’entreprise ne sont pas mauvais, alors il y aura une raison de maintenir le site en vie.
Mais si l’entreprise est sur une mauvaise pente et n’a plus d’argent, c’est tout le site qu’elle gère qui mourra, tout simplement. Renren en est un exemple typique.
D’un point de vue opérationnel, si une page web n’est pas visitée par quelques personnes tout au long de l’année, elle deviendra un fardeau pour l’entreprise, et le plus rationnel d’un point de vue économique sera de la supprimer — et ce même si l’entreprise n’a pas de problèmes financiers. Les premières années de Sohu ; le site NetEase dont le contenu a été essentiellement perdu ; ainsi que la disparition collective des forums hébergés dans Tianya en sont de bons exemples.
Si une entreprise est sur une mauvaise pente et n’a plus d’argent, c’est tout le site qu’elle gère qui mourra.
He Jiayan
Deuxièmement, les raisons réglementaires.
En général, la réglementation sur Internet augmente progressivement et devient de plus en plus stricte. Le contenu qui pouvait exister légalement auparavant ne répond plus aux exigences réglementaires ; et ce qui pouvait exister dans la grise auparavant a depuis basculé dans la zone rouge. Tous ces contenus sont directement supprimés.
Il y a aussi des cas où la polarisation de l’opinion publique est devenue plus forte avec le temps et où un contenu qui était « tout à fait normal » est devenu très sensible pour l’opinion publique. Même s’il n’est pas illégal, il peut intensifier le conflit et créer de la confusion — si bien que le régulateur peut demander qu’il soit éliminé.
Au-delà des autorités officielles, les internautes en colère agissent parfois comme des modérateurs ou au contraire des faiseurs d’opinion. Ils peuvent faire sortir de l’ombre quelque chose que quelqu’un a posté en passant il y a plus de dix ans, s’y accrocher et cyber-harceler l’auteur jusqu’à sa « mort sociale ».
En Chine, l’effet le plus important de la réglementation n’est donc pas tant ce que font les régulateurs ou les attaques des internautes en colère que l’« autocensure » qu’ils provoquent au sein des entreprises et chez les particuliers.
En Chine, l’effet le plus important de la réglementation n’est donc pas tant ce que font les régulateurs ou les attaques des internautes en colère que l’« autocensure » qu’ils provoquent au sein des entreprises et chez les particuliers.
He Jiayan
Personne ne sait si un contenu sur un site web ou un mot prononcé par quelqu’un entraînera la mort de cette personne dans plusieurs années. Le meilleur moyen de survivre est donc de supprimer toutes ces « bombes à retardement » potentielles — c’est-à-dire de fermer le site web ou d’en supprimer tout le contenu.
Bien entendu, les autres causes sont nombreuses qui peuvent expliquer la disparition d’anciennes pages web.
Peu après la dissolution de l’ex-Yougoslavie, tous les contenus web hébergés sous le nom de domaine international « .yu » — abréviation de Yougoslavie — ont disparu. Un autre exemple est la disparition de sites de musique et de films qui étaient autrefois facilement disponibles pour le téléchargement, en raison du renforcement de la protection des droits d’auteur. Certaines organisations et des individus, pour des raisons purement personnelles, ne veulent parfois simplement plus montrer leurs informations au public et ferment donc leurs sites web officiels ou leurs pages d’accueil personnelles.
Mais ces raisons sont secondaires et localisées.
La disparition systématique et à grande échelle du contenu Internet dans son ensemble est principalement due aux lois économiques et à l’autocensure.
La disparition systématique et à grande échelle du contenu Internet dans son ensemble est principalement due aux lois économiques et à l’autocensure.
He Jiayan
Au fond, tout se passe comme si le contenu d’Internet — à l’instar de la vie — était régi par la théorie de l’évolution. Il n’a qu’un seul critère d’existence : attirer le plus d’attention possible au moindre coût.
Lorsqu’un contenu est capable d’attirer suffisamment d’attention, et que le coût de maintien de ce contenu — en ce compris le coût économique, le coût de la réglementation et le coût de la lutte contre la réglementation — est faible, ce contenu a des chances de survivre sur Internet. Il est probable qu’il changera même de support — par exemple en passant du texte à l’image, de l’image fixe à l’image animée, de l’image animée à la vidéo et, à l’avenir, peut-être de la vidéo bidimensionnelle à la vidéo holographique tridimensionnelle, et ainsi de suite. La plateforme qui sert de véhicule à ce contenu changera également. On passera du portail au forum, aux blogs personnels, au microblogging — et à l’avenir peut-être à une plateforme dont nous ignorons tout pour l’instant.
Lorsqu’un contenu ne peut plus attirer suffisamment l’attention ou que le coût de maintenance de ce contenu est trop élevé, il disparaîtra d’Internet. La disparition collective de l’Internet traditionnel, avec des ordinateurs servant de terminaux de navigation et des pages web comme supports, est simplement le résultat inévitable de cette « concurrence évolutive pour l’information ».
La disparition collective de l’Internet traditionnel est simplement le résultat inévitable d’une « concurrence évolutive pour l’information ».
He Jiayan
Darwin nous a appris que la clef de l’évolution biologique était la « sélection naturelle, la survie du plus apte ». La clef de l’évolution du contenu d’Internet est la « concurrence de l’information, la sélection de l’attention ». En raison de l’effet de réseau, cette concurrence est dix mille fois plus féroce que dans la nature — dix mille fois plus cruelle. L’Internet traditionnel n’emportera pas l’extinction d’une seule espèce mais l’extinction de la quasi-totalité du contenu.
À chaque nouvelle génération d’Internet, l’ancienne génération, arrimée à une structure obsolète, s’effondrera. C’est la destinée de tous les sites web et de tous leurs contenus.
Si Internet est l’avenir de la civilisation, alors notre génération n’aura pas d’histoire — parce qu’Internet n’aura laissé de nous aucune trace.
Si Internet est l’avenir de la civilisation, alors notre génération n’aura pas d’histoire — parce qu’Internet n’aura laissé de nous aucune trace.
He Jiayan
« Pas d’histoire ». Est-ce si important ?
Bien sûr que oui.
Pour écrire un article sur Shao Yibo, j’ai essayé par tous les moyens de mettre la main sur la vidéo originale de la participation de Shao Yibo à l’émission « Boshi Tang » en 2007 ainsi que les posts de sa femme, Bao Jiaxin, sur le site Baby Tree, postés depuis quelques années sous le pseudonyme de « Wen Ai Mummy ». Je ne suis pas parvenu à les retrouver — et je ne peux que le regretter.
Bien que l’article « Red Dust Has Forgotten Shao Yibo » soit toujours très populaire — avec plus de 700 000 lecteurs et 20 000 retweets en seulement une semaine — je suis presque sûr que j’ai dû passer à côté d’informations très importantes et que la qualité de l’article aurait été meilleure si j’avais eu accès à de telles informations.
Vous vous dites peut-être : « cela n’est utile qu’aux chercheurs et aux rédacteurs comme He Jiayan, je n’écris pas d’articles de ce genre, et ce n’est pas comme si cela n’affectait. »
Vraiment ?
Si nous ne pouvons plus avoir accès à tous les discours de Jack Ma, tous les articles de Ren Zhengfei, My Father and Mother et The Spring River Flows East, et tous les messages de Duan Yongping dans Snowball, ne seriez-vous pas un peu triste ?
He Jiayan fait ici référence à des lieux communs de la culture populaire chinoise. Ren Zhengfei est le directeur général de Huawei, My Father and Mother est un film romantique sorti en 2013 et The Spring River Flows East un film datant de 1947 considéré comme un classique du cinéma chinois.
Vous me direz que vous êtes insensibles.
Alors, si nous ne pouvons plus chercher le numéro de Huang Zheng, si nous ne pouvons plus voir les messages de Zhang Yiming ou de Wang Xing, est-ce que vous n’éprouverez pas un peu de regret ?
Vous m’assurerez que vous ne vous sentez pas désolé non plus.
Si un jour, Zhihu disparaît comme Tianya Forum, Douban s’efface comme RenRen, B-site se vide comme Sina Blog — ne ressentirez-vous pas un peu de chagrin ?
Si un jour, les pages Internet de votre blogueur préféré affichent que « l’auteur a choisi de n’afficher que la moitié des posts de l’année » ou que « ce blog n’est plus visible », si vous lisez souvent que « ce compte a été bloqué », que « le contenu ne peut être affiché », si vous recherchez certaines informations dans Shake Voice ou Xiaohongshu, et que les résultats affichent que « l’auteur a effacé tout le contenu »…
Cela ne vous attristera-t-il pas — ne serait-ce qu’un instant ?
Les générations de l’Internet traditionnel, nées dans les années 1970 et 1980 ne peuvent plus retrouver leur histoire. Leurs traces en ont pratiquement disparu.
Les générations de l’Internet traditionnel, nées dans les années 1970 et 1980 ne peuvent plus retrouver leur histoire. Leurs traces en ont pratiquement disparu.
He Jiayan
La nouvelle génération peut encore garder les messages de cercles d’amis privés, mais même de cercle d’amis est, de plus en plus, « visible seulement trois jours ». Messages éphémères… — jusqu’à ce que tout s’efface.
La seule chose qui produit encore du contenu de manière frénétique, c’est le marketing en cascade.
Mais à l’avenir, il y a fort à parier que même ces messages marketing finiront par disparaître.
Si quelque chose est important pour nous et qu’il est en train de disparaître, existe-t-il un moyen de le sauver ?
Certains ont essayé de le faire.
Il existe aux États-Unis un site web appelé Internet Archive, qui se traduit en chinois par « 互联网档案馆 » et qui préserve un grand nombre de pages web originales. Mais pour avoir essayé de l’utiliser, les pages web originales en chinois sont très peu sauvegardées. L’utilisation en est très difficile, les fonctionnalités de recherche assez primitives et inefficaces. En définitive, quantitativement, elles n’ont pas permis de sauvegarder grand-chose.
D’un point de vue technique, il ne devrait pas être difficile de sauvegarder toutes les pages web de l’Internet chinois jusqu’à l’essor de l’Internet mobile au cours des dix dernières années. Et le coût n’en serait pas élevé. Après tout, si on la compare à l’ère actuelle de l’Internet, où la vidéo est hégémonique, cette ère faite de pages web au graphisme limité est négligeable en termes d’espace.
Si on la compare à l’ère actuelle de l’Internet, où la vidéo est hégémonique, cette ère faite de pages web au graphisme limité est négligeable en termes d’espace.
He Jiayan
La question est de savoir qui saura le faire, et mû par quoi.
Les entreprises ne le feront pas. Elles n’y auraient pas d’intérêt commercial.
Le gouvernement pourrait être en mesure de créer des archives qui conservent toutes les pages — tout comme il construit des bibliothèques et des musées. Mais dépenserait-il de l’argent pour cela ? Il semble qu’il n’y ait pas d’autre raison que de préserver l’histoire. Or même si le gouvernement le faisait, cela ne changerait rien pour les utilisateurs ordinaires d’Internet, car ces archives nécessiteraient un traitement immense concernant les données personnelles et ne seraient accessibles qu’à quelques-uns pour éviter précisément tout abus dans l’utilisation de ces données.
D’ailleurs, même si un organe quelconque était disposé à le faire, il serait désormais trop tard. Après l’essor de l’Internet mobile, selon une estimation approximative, plus de 99 % du contenu de l’Internet chinois traditionnel devrait avoir disparu.
D’une certaine manière, les articles que j’ai rédigés ont contribué à la préservation de l’histoire de leurs sujets. Si je n’avais pas écrit sur eux, une grande partie de cette histoire serait déjà introuvable en ligne. Pourtant il ne s’agit pas d’informations originales, mais seulement d’informations de seconde main que j’ai consolidées.
Après l’essor de l’Internet mobile, selon une estimation approximative, plus de 99 % du contenu de l’Internet chinois traditionnel devrait avoir disparu.
He Jiayan
Aujourd’hui, sur tous les événements majeurs qui se sont produits au cours de la première décennie de ce siècle, toutes les célébrités qui ont laissé des traces profondes, les informations que l’on peut encore trouver sur l’Internet chinois sont presque toujours des informations de seconde main éditées par des médias pure player — ou même des informations qui ont été maintes fois reprises et republiées et qui sont depuis longtemps complètement différentes de leur forme originale.
Les rapports originaux, les vidéos originales, les discours originaux, les observations originales des internautes, les commentaires originaux — tout cela a disparu.
Dans quelques années, toutes ces informations de seconde main auront également disparu. Tout se passe comme si ces événements n’avaient jamais eu lieu. Comme si ces personnes n’avaient jamais existé.
Il n’y a rien d’autre à faire que d’accepter la réalité.
À l’ère d’Internet, les vingt premières années du XXIe siècle seront vingt années sans archives historiques.
À l’ère d’Internet, les vingt premières années du XXIe siècle seront vingt années sans archives historiques.
He Jiayan
Si vous pouvez encore voir des informations anciennes de l’Internet chinois aujourd’hui, ce n’est que la dernière lueur du crépuscule.
Si vous êtes saisis par leur nature éphémère, vous pourrez soupirer comme Faust sur son lit de mort implorant l’instant : « Arrête-toi, tu es si beau ! »
Mais cette lueur sera bientôt engloutie par le temps et tombera dans le vide — en même temps que votre exclamation.
Il n’y a pas d’échappatoire.
Presque tout ce que vous voyez et créez maintenant — cet article, cette plateforme — finira par se noyer dans le vide.